Page 13 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 13
Introduction 3
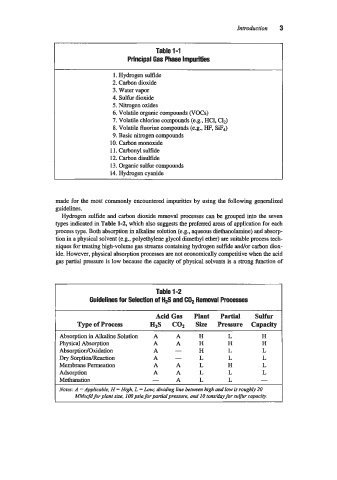
Table 1-1
Principal Gas Phase Impurities
1. Hydrogen sulfide
2. Carbon dioxide
3. Water vapor
4. sulfur dioxide
5. Nitrogen oxides
6. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
7. Volatile chlorine compounds (e.g., HC1, C1d
8. Volatile fluorine compounds (e.g., HF, SiF,)
9. Basic nitrogen compounds
10. Carbon monoxide
1 1. Carbonyl sulfide
12. Carbon disulfide
13. Organic sulfur compounds
14. Hydrogen cyanide
made for the most commonly encountered impurities by using the following generalized
guidelines.
Hydrogen sulfide and carbon dioxide removal processes can be grouped into the seven
types indicated in Table 1-2, which also suggests the preferred areas of application for each
process type. Both absorption in alkalime solution (e.g., aqueous diethanolamine) and absorp-
tion in a physical solvent (e.g., polyethylene glycol dimethyl ether) are suitable process tech-
niques for treating high-volume gas streams containing hydrogen sulfide andor carbon diox-
ide. However, physical absorption processes are not economically competitive when the acid
gas partial pressure is low because the capacity of physical solvents is a strong function
Table 1-2
Guidelines for Selection of H2S and C& Removal Processes
AcidGas Plant Partial Sulfur
Type of Process HzS COz Size Pressure Capacity
Absorption in Alkaline Solution A A H L H
Physical Absorption A A H H H
AbsorptiodOxidation A - H L L
Dry SorptionlReaction A - L L L
Membrane Permeation A A L H L
Adsorption A A L L L
Methanation - A L L -
Notes: A =Applicable, H = High, L =Low; dividing line between high and low is roughly 20
MMscfd for plant sue, 100 psia for partial pressure. and IO tondday for sulfur capaciv.