Page 59 - Gas Purification 5E
P. 59
Alkanolamines-for Hydrogen Surfide and Carbon Dioxide Removal 49
case, sufficient data and operating experience with several alkanolamhes are on hand to pennit
a judicious selection of the treating solution for a wide range of conditions. In many cases,
process requirements can be met by a numbex of dEerent amiues [or other processes) and an
economic analysis is required A comparison of holamines used for gas purification, based
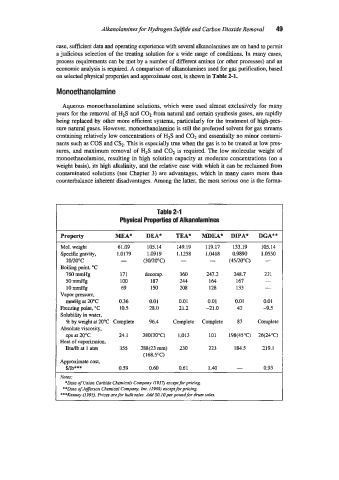
on selected physical Properties and appro-ximate cost, is shown in Table 2-1.
Monoethanolamine
Aqueous monoethanolamine solutions, which were used almost exclusively for many
years for the removal of H2S and C02 from natural and certain synthesis gases. are rapidly
being replaced by other more efficient systems. particularly for the treatment of high-pres-
sure natural gases. However, monoethanolamine is still the preferred solvent for gas streams
containing relatively low concentrations of H2S and CO: and essentially no minor contami-
nants such as COS and CS2. This is especially true when the gas is to be treated at low pres-
sures, and maximum removal of H2S and COz is required. The low molecular weight of
monoethanolamine, resulting in high solution capacity at moderate concentrations (on a
weight basis), its high alkakity, and the relative ease with which it can be reclaimed from
conlaminated solutions (see Chapter 3) are advantages, which in many cases more than
counterbalance inherent disadvantages. Among the latter, the most serious one is the forma-
Table 2-1
Physical Properties of Albnolamines
Property MEA* DEA* TEA* MDEA* DPA* DGA**
Mol. weight 61.09 105.14 149.19 119.17 133.19 105.14
Specific .gravity, 1.0179 1.0919 1.1258 1.0418 0.9890 1.0550
W2"C - (3o/u)=cj - - (45/20"C) -
Boiling point, "C
760 mmHg 171 bmp. 360 247.2 248.7 21 1
50 mmHg 100 187 7@ 164 167 -
10 mmHg 69 150 108 128 133 -
Vapor pressure,
mmHg at 20°C 0.36 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01
Freezing point, =c 10.5 28.0 21.2 -21.0 42 -9.5
Solubility in water,
5% by weight at 10°C Complete 96.4 Complete Complete 87 Complete
Absolute viscosity.
cps at 20°C 21.1 38O(3O0C) 1,013 101 198(45"C) 26(24'C)
Heat of vaporization.
Btu/lb at 1 atm 355 288(23mm) 230 223 184.5 219.1
(168.5'C)
Approximate cost,
Wb*** 0.59 0.60 0.61 1-40 - 0.93
YO^:
*Data of L%im Carbide Chemicals ConPany f1957, acq forpricing.
**Data of Je&rson Chemical Companyl Inc. N969) aceptforp&ing.
***Kenney (1993). Priw are for bulksales. AddSO.lOperpmdfbr dium sales.