Page 13 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 13
xii Introduction
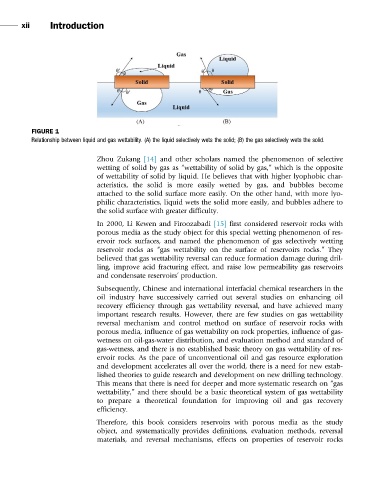
FIGURE 1
Relationship between liquid and gas wettability. (A) the liquid selectively wets the solid; (B) the gas selectively wets the solid.
Zhou Zukang [14] and other scholars named the phenomenon of selective
wetting of solid by gas as “wettability of solid by gas,” which is the opposite
of wettability of solid by liquid. He believes that with higher lyophobic char-
acteristics, the solid is more easily wetted by gas, and bubbles become
attached to the solid surface more easily. On the other hand, with more lyo-
philic characteristics, liquid wets the solid more easily, and bubbles adhere to
the solid surface with greater difficulty.
In 2000, Li Kewen and Firoozabadi [15] first considered reservoir rocks with
porous media as the study object for this special wetting phenomenon of res-
ervoir rock surfaces, and named the phenomenon of gas selectively wetting
reservoir rocks as “gas wettability on the surface of reservoirs rocks.” They
believed that gas wettability reversal can reduce formation damage during dril-
ling, improve acid fracturing effect, and raise low permeability gas reservoirs
and condensate reservoirs’ production.
Subsequently, Chinese and international interfacial chemical researchers in the
oil industry have successively carried out several studies on enhancing oil
recovery efficiency through gas wettability reversal, and have achieved many
important research results. However, there are few studies on gas wettability
reversal mechanism and control method on surface of reservoir rocks with
porous media, influence of gas wettability on rock properties, influence of gas-
wetness on oil-gas-water distribution, and evaluation method and standard of
gas-wetness, and there is no established basic theory on gas wettability of res-
ervoir rocks. As the pace of unconventional oil and gas resource exploration
and development accelerates all over the world, there is a need for new estab-
lished theories to guide research and development on new drilling technology.
This means that there is need for deeper and more systematic research on “gas
wettability,” and there should be a basic theoretical system of gas wettability
to prepare a theoretical foundation for improving oil and gas recovery
efficiency.
Therefore, this book considers reservoirs with porous media as the study
object, and systematically provides definitions, evaluation methods, reversal
materials, and reversal mechanisms, effects on properties of reservoir rocks