Page 20 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 20
4 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
1 1
Water-wetting Water-wetting
0 0
Concentration Wetting index Concentration
Wetting index
Oil-wetting Oil-wetting
–1 –1
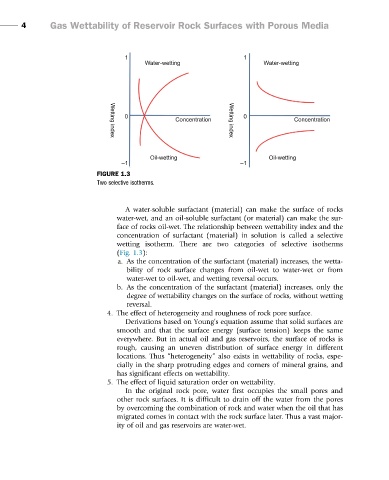
FIGURE 1.3
Two selective isotherms.
A water-soluble surfactant (material) can make the surface of rocks
water-wet, and an oil-soluble surfactant (or material) can make the sur-
face of rocks oil-wet. The relationship between wettability index and the
concentration of surfactant (material) in solution is called a selective
wetting isotherm. There are two categories of selective isotherms
(Fig. 1.3):
a. As the concentration of the surfactant (material) increases, the wetta-
bility of rock surface changes from oil-wet to water-wet or from
water-wet to oil-wet, and wetting reversal occurs.
b. As the concentration of the surfactant (material) increases, only the
degree of wettability changes on the surface of rocks, without wetting
reversal.
4. The effect of heterogeneity and roughness of rock pore surface.
Derivations based on Young’s equation assume that solid surfaces are
smooth and that the surface energy (surface tension) keeps the same
everywhere. But in actual oil and gas reservoirs, the surface of rocks is
rough, causing an uneven distribution of surface energy in different
locations. Thus “heterogeneity” also exists in wettability of rocks, espe-
cially in the sharp protruding edges and corners of mineral grains, and
has significant effects on wettability.
5. The effect of liquid saturation order on wettability.
In the original rock pore, water first occupies the small pores and
other rock surfaces. It is difficult to drain off the water from the pores
by overcoming the combination of rock and water when the oil that has
migrated comes in contact with the rock surface later. Thus a vast major-
ity of oil and gas reservoirs are water-wet.