Page 22 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 22
6 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
Gas phase Gas phase
θ < 90º
h Liquid phase
θ = 90º
θ < 90º
h<0
phase
Liquid
Liquid
phase
Strong liquid-wetting Intermediate gas-wetting Gas-wetting
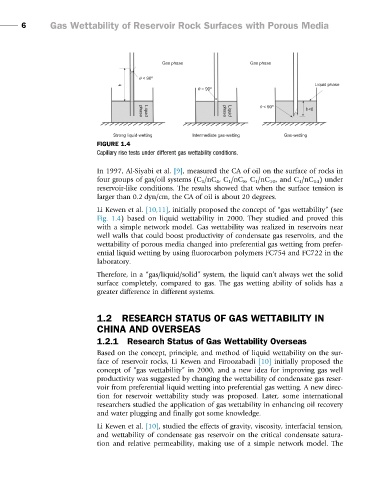
FIGURE 1.4
Capillary rise tests under different gas wettability conditions.
In 1997, Al-Siyabi et al. [9], measured the CA of oil on the surface of rocks in
four groups of gas/oil systems (C 1 /nC 4 ,C 1 /nC 8 ,C 1 /nC 10 ,and C 1 /nC 14 ) under
reservoir-like conditions. The results showed that when the surface tension is
larger than 0.2 dyn/cm, the CA of oil is about 20 degrees.
Li Kewen et al. [10,11], initially proposed the concept of “gas wettability” (see
Fig. 1.4) based on liquid wettability in 2000. They studied and proved this
with a simple network model. Gas wettability was realized in reservoirs near
well walls that could boost productivity of condensate gas reservoirs, and the
wettability of porous media changed into preferential gas wetting from prefer-
ential liquid wetting by using fluorocarbon polymers FC754 and FC722 in the
laboratory.
Therefore, in a “gas/liquid/solid” system, the liquid can’t always wet the solid
surface completely, compared to gas. The gas wetting ability of solids has a
greater difference in different systems.
1.2 RESEARCH STATUS OF GAS WETTABILITY IN
CHINA AND OVERSEAS
1.2.1 Research Status of Gas Wettability Overseas
Based on the concept, principle, and method of liquid wettability on the sur-
face of reservoir rocks, Li Kewen and Firoozabadi [10] initially proposed the
concept of “gas wettability” in 2000, and a new idea for improving gas well
productivity was suggested by changing the wettability of condensate gas reser-
voir from preferential liquid wetting into preferential gas wetting. A new direc-
tion for reservoir wettability study was proposed. Later, some international
researchers studied the application of gas wettability in enhancing oil recovery
and water plugging and finally got some knowledge.
Li Kewen et al. [10], studied the effects of gravity, viscosity, interfacial tension,
and wettability of condensate gas reservoir on the critical condensate satura-
tion and relative permeability, making use of a simple network model. The