Page 80 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 80
64 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
120
Surface energy (mJ/m 2 ) 80
100
60
40
20
0 150
0 100
50 50
100
150
Water angle (º) 0 N-hexadecane angle (º)
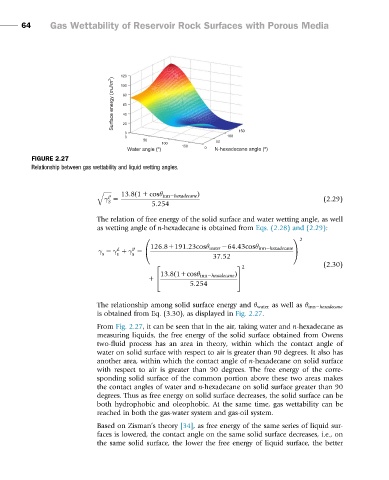
FIGURE 2.27
Relationship between gas wettability and liquid wetting angles.
q ffiffiffiffiffi 13:8ð1 1 cosθ inn2hexadecane Þ
P
γ 5 (2.29)
S
5:254
The relation of free energy of the solid surface and water wetting angle, as well
as wetting angle of n-hexadecane is obtained from Eqs. (2.28) and (2.29):
0 1 2
d
P
γ 5 γ 1 γ 5 @ 126:81191:23cosθ water 264:43cosθ inn2hexadecane A
s s s
37:52
(2.30)
2 3 2
13:8ð11cosθ inn2hexadecane Þ
1 4 5
5:254
The relationship among solid surface energy and θ water as well as θ inn2hexadecane
is obtained from Eq. (3.30), as displayed in Fig. 2.27.
From Fig. 2.27, it can be seen that in the air, taking water and n-hexadecane as
measuring liquids, the free energy of the solid surface obtained from Owens
two-fluid process has an area in theory, within which the contact angle of
water on solid surface with respect to air is greater than 90 degrees. It also has
another area, within which the contact angle of n-hexadecane on solid surface
with respect to air is greater than 90 degrees. The free energy of the corre-
sponding solid surface of the common portion above these two areas makes
the contact angles of water and n-hexadecane on solid surface greater than 90
degrees. Thus as free energy on solid surface decreases, the solid surface can be
both hydrophobic and oleophobic. At the same time, gas wettability can be
reached in both the gas-water system and gas-oil system.
Based on Zisman’s theory [34], as free energy of the same series of liquid sur-
faces is lowered, the contact angle on the same solid surface decreases, i.e., on
the same solid surface, the lower the free energy of liquid surface, the better