Page 76 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 76
60 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
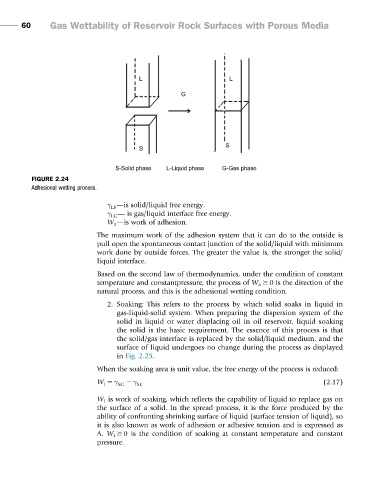
FIGURE 2.24
Adhesional wetting process.
γ —is solid/liquid free energy.
LS
γ — is gas/liquid interface free energy.
LG
W a —is work of adhesion.
The maximum work of the adhesion system that it can do to the outside is
pull open the spontaneous contact junction of the solid/liquid with minimum
work done by outside forces. The greater the value is, the stronger the solid/
liquid interface.
Based on the second law of thermodynamics, under the condition of constant
temperature and constantpressure, the process of W a $ 0 is the direction of the
natural process, and this is the adhesional wetting condition.
2. Soaking: This refers to the process by which solid soaks in liquid in
gas-liquid-solid system. When preparing the dispersion system of the
solid in liquid or water displacing oil in oil reservoir, liquid soaking
the solid is the basic requirement. The essence of this process is that
the solid/gas interface is replaced by the solid/liquid medium, and the
surface of liquid undergoes no change during the process as displayed
in Fig. 2.25.
When the soaking area is unit value, the free energy of the process is reduced:
W i 5 γ 2 γ (2.17)
SG SL
W i is work of soaking, which reflects the capability of liquid to replace gas on
the surface of a solid. In the spread process, it is the force produced by the
ability of confronting shrinking surface of liquid (surface tension of liquid), so
it is also known as work of adhesion or adhesive tension and is expressed as
A. W i $ 0 is the condition of soaking at constant temperature and constant
pressure.