Page 74 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 74
58 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
the strength of gas wettability has something to do with the nature of liquid
phase in gas/liquid/solid.
The relationship between gas wettability and Zonyl8740 solution concentration
is consistent for bubble capture method and sessile drop method. However, the
degree of gas wettability is inconsistent, which is related to the saturation history
of the solid surface. The sessile drop method involves a process of solid/liquid
interface replacing solid/gas interface, while the bubble capture method involves
a process of solid/gas interface replacing solid/liquid interface.
2.3.3 Experimental Verification of Gas Wettability
Evaluation Method
In order to further prove the effectiveness of established gas wettability evalua-
tion methods, the capillary rise experiment has been adopted for experimental
verification for the two kinds of visual quantitative evaluation methods [26].
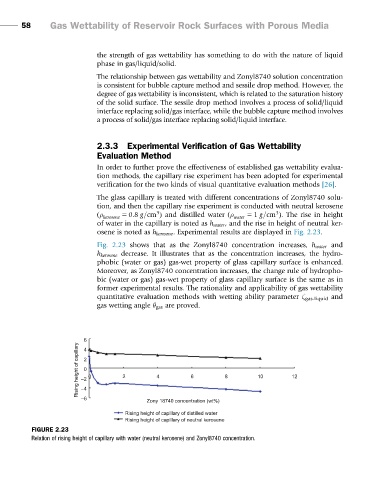
The glass capillary is treated with different concentrations of Zonyl8740 solu-
tion, and then the capillary rise experiment is conducted with neutral kerosene
ðρ 5 0:8 g=cm Þ and distilled water ðρ 5 1 g=cm Þ. The rise in height
3
3
kerosene water
of water in the capillary is noted as h water , and the rise in height of neutral ker-
osene is noted as h kerosene . Experimental results are displayed in Fig. 2.23.
Fig. 2.23 shows that as the Zonyl8740 concentration increases, h water and
h kerosene decrease. It illustrates that as the concentration increases, the hydro-
phobic (water or gas) gas-wet property of glass capillary surface is enhanced.
Moreover, as Zonyl8740 concentration increases, the change rule of hydropho-
bic (water or gas) gas-wet property of glass capillary surface is the same as in
former experimental results. The rationality and applicability of gas wettability
quantitative evaluation methods with wetting ability parameter ζ gas-liquid and
gas wetting angle θ gas are proved.
6 4
Rising height of capillary –2 2 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12
–4
–6
Zony 18740 concentration (wt%)
Rising height of capillary of distilled water
Rising height of capillary of neutral kerosene
FIGURE 2.23
Relation of rising height of capillary with water (neutral kerosene) and Zonyl8740 concentration.