Page 70 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 70
54 Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
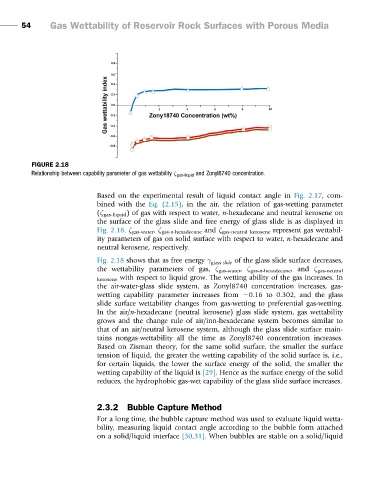
FIGURE 2.18
Relationship between capability parameter of gas wettability ζ gas-liquid and Zonyl8740 concentration.
Based on the experimental result of liquid contact angle in Fig. 2.17, com-
bined with the Eq. (2.15), in the air, the relation of gas-wetting parameter
(ζ gas-liquid ) of gas with respect to water, n-hexadecane and neutral kerosene on
the surface of the glass slide and free energy of glass slide is as displayed in
Fig. 2.18. ζ gas-water , ζ gas-n-hexadecane and ζ gas-neutral kerosene represent gas wettabil-
ity parameters of gas on solid surface with respect to water, n-hexadecane and
neutral kerosene, respectively.
Fig. 2.18 shows that as free energy γ glass slide of the glass slide surface decreases,
the wettability parameters of gas, ζ gas-water , ζ gas-n-hexadecane , and ζ gas-neutral
kerosene with respect to liquid grow. The wetting ability of the gas increases. In
the air-water-glass slide system, as Zonyl8740 concentration increases, gas-
wetting capability parameter increases from 20.16 to 0.302, and the glass
slide surface wettability changes from gas-wetting to preferential gas-wetting.
In the air/n-hexadecane (neutral kerosene) glass slide system, gas wettability
grows and the change rule of air/inn-hexadecane system becomes similar to
that of an air/neutral kerosene system, although the glass slide surface main-
tains nongas-wettability all the time as Zonyl8740 concentration increases.
Based on Zisman theory, for the same solid surface, the smaller the surface
tension of liquid, the greater the wetting capability of the solid surface is, i.e.,
for certain liquids, the lower the surface energy of the solid, the smaller the
wetting capability of the liquid is [29]. Hence as the surface energy of the solid
reduces, the hydrophobic gas-wet capability of the glass slide surface increases.
2.3.2 Bubble Capture Method
For a long time, the bubble capture method was used to evaluate liquid wetta-
bility, measuring liquid contact angle according to the bubble form attached
on a solid/liquid interface [30,31]. When bubbles are stable on a solid/liquid