Page 67 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 67
Evaluation Methods and Influencing Factors CHAPTER 2 51
0.8
Preferential gas-wetting
0.6
Intermediate gas-wetting
0.4
0.2
ζ gas-wetting 0.0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
Non-gas-wetting
–0.2
–0.4
–0.6
–0.8
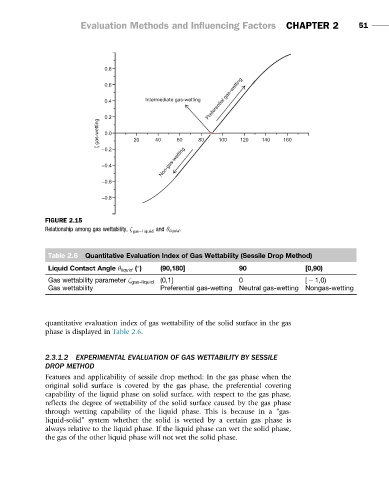
FIGURE 2.15
Relationship among gas wettability, ζ gas2liquid and θ liquid .
Table 2.6 Quantitative Evaluation Index of Gas Wettability (Sessile Drop Method)
Liquid Contact Angle θ liquid ( ) (90,180] 90 [0,90)
Gas wettability parameter ζ gas-liquid (0,1] 0 [ 2 1,0)
Gas wettability Preferential gas-wetting Neutral gas-wetting Nongas-wetting
quantitative evaluation index of gas wettability of the solid surface in the gas
phase is displayed in Table 2.6.
2.3.1.2 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION OF GAS WETTABILITY BY SESSILE
DROP METHOD
Features and applicability of sessile drop method: In the gas phase when the
original solid surface is covered by the gas phase, the preferential covering
capability of the liquid phase on solid surface, with respect to the gas phase,
reflects the degree of wettability of the solid surface caused by the gas phase
through wetting capability of the liquid phase. This is because in a “gas-
liquid-solid” system whether the solid is wetted by a certain gas phase is
always relative to the liquid phase. If the liquid phase can wet the solid phase,
the gas of the other liquid phase will not wet the solid phase.