Page 71 - Gas Wettability of Reservoir Rock Surfaces with Porous Media
P. 71
Evaluation Methods and Influencing Factors CHAPTER 2 55
(A) (B) (C)
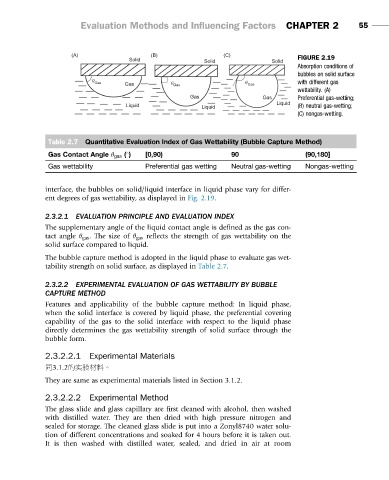
Solid Solid Solid FIGURE 2.19
Absorption conditions of
bubbles on solid surface
θ
Gas θ θ with different gas
Gas Gas Gas
wettability. (A)
Gas Gas Preferential gas-wetting;
Liquid
Liquid Liquid (B) neutral gas-wetting;
(C) nongas-wetting.
Table 2.7 Quantitative Evaluation Index of Gas Wettability (Bubble Capture Method)
Gas Contact Angle θ gas ( ) [0,90) 90 (90,180]
Gas wettability Preferential gas wetting Neutral gas-wetting Nongas-wetting
interface, the bubbles on solid/liquid interface in liquid phase vary for differ-
ent degrees of gas wettability, as displayed in Fig. 2.19.
2.3.2.1 EVALUATION PRINCIPLE AND EVALUATION INDEX
The supplementary angle of the liquid contact angle is defined as the gas con-
tact angle θ gas . The size of θ gas reflects the strength of gas wettability on the
solid surface compared to liquid.
The bubble capture method is adopted in the liquid phase to evaluate gas wet-
tability strength on solid surface, as displayed in Table 2.7.
2.3.2.2 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION OF GAS WETTABILITY BY BUBBLE
CAPTURE METHOD
Features and applicability of the bubble capture method: In liquid phase,
when the solid interface is covered by liquid phase, the preferential covering
capability of the gas to the solid interface with respect to the liquid phase
directly determines the gas wettability strength of solid surface through the
bubble form.
2.3.2.2.1 Experimental Materials
同3.1.2的实验材料。
They are same as experimental materials listed in Section 3.1.2.
2.3.2.2.2 Experimental Method
The glass slide and glass capillary are first cleaned with alcohol, then washed
with distilled water. They are then dried with high pressure nitrogen and
sealed for storage. The cleaned glass slide is put into a Zonyl8740 water solu-
tion of different concentrations and soaked for 4 hours before it is taken out.
It is then washed with distilled water, sealed, and dried in air at room