Page 254 - Gas Adsorption Equilibria
P. 254
240 Chapter 5
2.2 Outline of Theory
In this section we present relations between the moment of inertia (J), of
the rotational pendulum and measurable parameters of its slow, damped
harmonic oscillations, namely the frequency and the logarithmic
decrement As the geometry of the pendulum normally is known, from
these relations, set up for oscillations in both vacuum and in a sorptive gas
atmosphere, the mass of the pendulum and hence the mass of an adsorbed
phase included in it can be calculated – at least in principle.
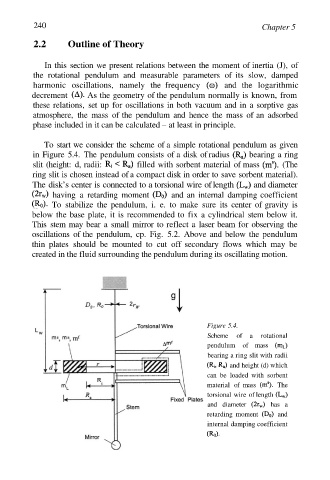
To start we consider the scheme of a simple rotational pendulum as given
in Figure 5.4. The pendulum consists of a disk of radius bearing a ring
slit (height: d, radii: filled with sorbent material of mass (The
ring slit is chosen instead of a compact disk in order to save sorbent material).
The disk’s center is connected to a torsional wire of length and diameter
having a retarding moment and an internal damping coefficient
To stabilize the pendulum, i. e. to make sure its center of gravity is
below the base plate, it is recommended to fix a cylindrical stem below it.
This stem may bear a small mirror to reflect a laser beam for observing the
oscillations of the pendulum, cp. Fig. 5.2. Above and below the pendulum
thin plates should be mounted to cut off secondary flows which may be
created in the fluid surrounding the pendulum during its oscillating motion.
Figure 5.4.
Scheme of a rotational
pendulum of mass
bearing a ring slit with radii
and height (d) which
can be loaded with sorbent
material of mass The
torsional wire of length
and diameter has a
retarding moment and
internal damping coefficient