Page 53 - Geochemistry of Oil Field Waters
P. 53
TITRIMETRIC METHODS 41
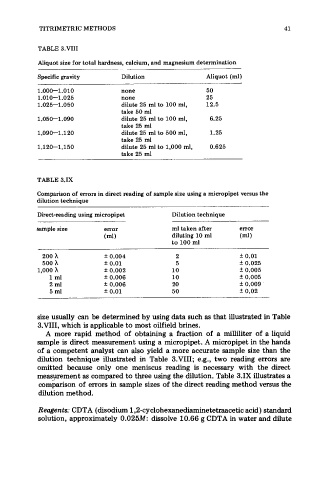
TABLE 3.VIII
Aliquot size for total hardness, calcium, and magnesium determination
Specific gravity Dilution Aliquot (ml)
1 .ooo--1.010 none 50
1.010-1.025 none 25
1.025-1 .O 50 dilute 25 ml to 100 ml, 12.5
take 50 ml
1.050-1.090 dilute 25 ml to 100 ml, 6.25
take 25 ml
1.090-1.1 20 dilute 25 ml to 500 ml, 1.25
take 25 ml
1.120-1.150 dilute 25 ml to 1,000 ml, 0.625
take 25 ml
TABLE 3.IX
Comparison of errors in direct reading of sample size using a micropipet versus the
dilution technique
Direct-reading using micropipet Dilution technique
sample size error ml taken after error
(ml) diluting 10 ml (ml)
to 100 ml
~~
200 h f 0.004 2 f 0.01
500 h f 0.01 5 f 0.025
1,000 h * 0.002 10 f 0.005
1 ml f 0.006 10 * 0.005
2 ml f 0.006 20 f 0.009
5 ml f 0.01 50 * 0.02
size usually can be determined by using data such as that illustrated in Table
3.VII1, which is applicable to most oilfield brines.
A more rapid method of obtaining a fraction of a milliliter of a liquid
sample is direct measurement using a micropipet. A micropipet in the hands
of a competent analyst can also yield a more accurate sample size than the
dilution technique illustrated in Table 3.VIII; e.g., two reading errors are
omitted because only one meniscus reading is necessary with the direct
measurement as compared to three using the dilution. Table 3.IX illustrates a
comparison of errors in sample sizes of the direct reading method versus the
dilution method.
Reagents: CDTA (disodium 1,2-cyclohexanediaminetet,raacetic acid) standard
solution, approximately 0.025M: dissolve 10.66 g CDTA in water and dilute