Page 128 - Geotechnical Engineering Soil and Foundation Principles and Practice
P. 128
Soil Minerals
Soil Minerals 123
Replacement of orbiting electrons from outer shells in atoms involves a stepwise
energy change, so X-rays have particular wavelengths. Other ‘‘white radiation’’
wavelengths also are produced and are used for medical X-rays, but for
diffraction measurements only a single wavelength can be used, so the rest are
filtered out.
The strongest monochromatic or single-wavelength X-rays are produced when a
position in the innermost or ‘‘K’’ atomic shell is replaced by one falling in from
the next outer shell, which generates ‘‘K radiation.’’ The most useful X-rays for
mineral identification are from a copper target and are therefore referred to as
‘‘copper K radiation.’’
6.2.3 Geometry of Diffraction
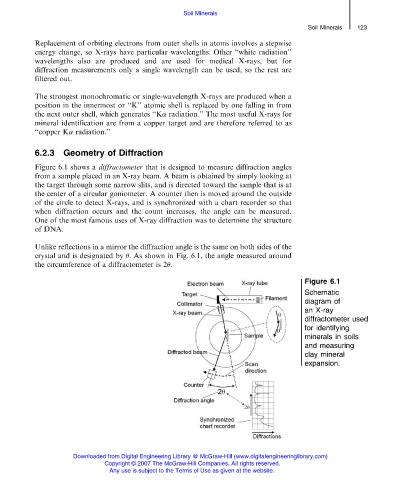
Figure 6.1 shows a diffractometer that is designed to measure diffraction angles
from a sample placed in an X-ray beam. A beam is obtained by simply looking at
the target through some narrow slits, and is directed toward the sample that is at
the center of a circular goniometer. A counter then is moved around the outside
of the circle to detect X-rays, and is synchronized with a chart recorder so that
when diffraction occurs and the count increases, the angle can be measured.
One of the most famous uses of X-ray diffraction was to determine the structure
of DNA.
Unlike reflections in a mirror the diffraction angle is the same on both sides of the
crystal and is designated by . As shown in Fig. 6.1, the angle measured around
the circumference of a diffractometer is 2 .
Figure 6.1
Schematic
diagram of
an X-ray
diffractometer used
for identifying
minerals in soils
and measuring
clay mineral
expansion.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.