Page 261 - Geotechnical Engineering Soil and Foundation Principles and Practice
P. 261
Soil Consistency and Engineering Classification
256 Geotechnical Engineering
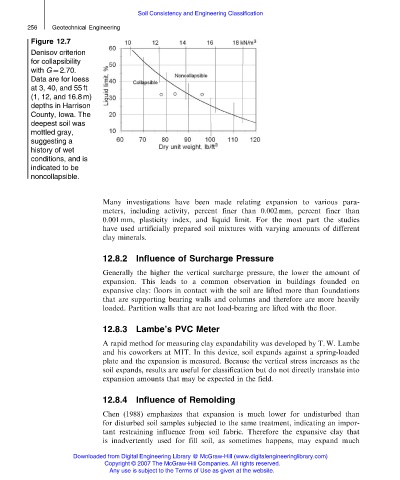
Figure 12.7
Denisov criterion
for collapsibility
with G ¼ 2.70.
Data are for loess
at 3, 40, and 55 ft
(1, 12, and 16.8 m)
depths in Harrison
County, Iowa. The
deepest soil was
mottled gray,
suggesting a
history of wet
conditions, and is
indicated to be
noncollapsible.
Many investigations have been made relating expansion to various para-
meters, including activity, percent finer than 0.002 mm, percent finer than
0.001 mm, plasticity index, and liquid limit. For the most part the studies
have used artificially prepared soil mixtures with varying amounts of different
clay minerals.
12.8.2 Influence of Surcharge Pressure
Generally the higher the vertical surcharge pressure, the lower the amount of
expansion. This leads to a common observation in buildings founded on
expansive clay: floors in contact with the soil are lifted more than foundations
that are supporting bearing walls and columns and therefore are more heavily
loaded. Partition walls that are not load-bearing are lifted with the floor.
12.8.3 Lambe’s PVC Meter
A rapid method for measuring clay expandability was developed by T. W. Lambe
and his coworkers at MIT. In this device, soil expands against a spring-loaded
plate and the expansion is measured. Because the vertical stress increases as the
soil expands, results are useful for classification but do not directly translate into
expansion amounts that may be expected in the field.
12.8.4 Influence of Remolding
Chen (1988) emphasizes that expansion is much lower for undisturbed than
for disturbed soil samples subjected to the same treatment, indicating an impor-
tant restraining influence from soil fabric. Therefore the expansive clay that
is inadvertently used for fill soil, as sometimes happens, may expand much
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.