Page 263 - Geotechnical Engineering Soil and Foundation Principles and Practice
P. 263
Soil Consistency and Engineering Classification
258 Geotechnical Engineering
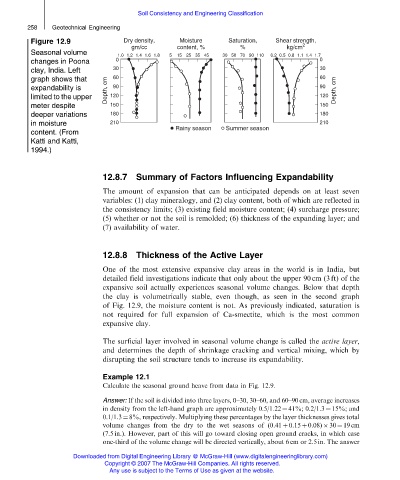
Figure 12.9
Seasonal volume
changes in Poona
clay, India. Left
graph shows that
expandability is
limited to the upper
meter despite
deeper variations
in moisture
content. (From
Katti and Katti,
1994.)
12.8.7 Summary of Factors Influencing Expandability
The amount of expansion that can be anticipated depends on at least seven
variables: (1) clay mineralogy, and (2) clay content, both of which are reflected in
the consistency limits; (3) existing field moisture content; (4) surcharge pressure;
(5) whether or not the soil is remolded; (6) thickness of the expanding layer; and
(7) availability of water.
12.8.8 Thickness of the Active Layer
One of the most extensive expansive clay areas in the world is in India, but
detailed field investigations indicate that only about the upper 90 cm (3 ft) of the
expansive soil actually experiences seasonal volume changes. Below that depth
the clay is volumetrically stable, even though, as seen in the second graph
of Fig. 12.9, the moisture content is not. As previously indicated, saturation is
not required for full expansion of Ca-smectite, which is the most common
expansive clay.
The surficial layer involved in seasonal volume change is called the active layer,
and determines the depth of shrinkage cracking and vertical mixing, which by
disrupting the soil structure tends to increase its expandability.
Example 12.1
Calculate the seasonal ground heave from data in Fig. 12.9.
Answer: If the soil is divided into three layers, 0–30, 30–60, and 60–90 cm, average increases
in density from the left-hand graph are approximately 0.5/1.22 ¼ 41%; 0.2/1.3 ¼ 15%; and
0.1/1.3 ¼ 8%, respectively. Multiplying these percentages by the layer thicknesses gives total
volume changes from the dry to the wet seasons of (0.41 þ 0.15 þ 0.08) 30 ¼ 19 cm
(7.5 in.). However, part of this will go toward closing open ground cracks, in which case
one-third of the volume change will be directed vertically, about 6 cm or 2.5 in. The answer
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.