Page 296 - Geotechnical Engineering Soil and Foundation Principles and Practice
P. 296
Compaction
Compaction 291
13.6.3 Relative Density Test
The Proctor density test originally was intended to simulate the action of a
sheepsfoot roller, but as previously mentioned, sheepsfoot rolling is not effective
in sandy soils containing little clay. Furthermore, the coarser the soil, the less
effective are capillary forces at preventing densification, so moisture content
becomes less critical.
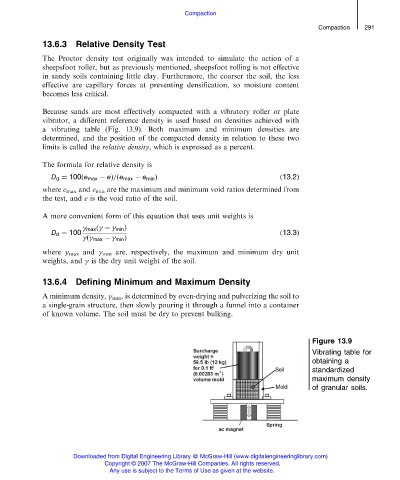
Because sands are most effectively compacted with a vibratory roller or plate
vibrator, a different reference density is used based on densities achieved with
a vibrating table (Fig. 13.9). Both maximum and minimum densities are
determined, and the position of the compacted density in relation to these two
limits is called the relative density, which is expressed as a percent.
The formula for relative density is
D d ¼ 100 e max eð Þ= e max e min Þ ð13:2Þ
ð
where e max and e min are the maximum and minimum void ratios determined from
the test, and e is the void ratio of the soil.
A more convenient form of this equation that uses unit weights is
max
min Þ
ð
D d ¼ 100 ð13:3Þ
max
min Þ
ð
where
max and
min are, respectively, the maximum and minimum dry unit
weights, and
is the dry unit weight of the soil.
13.6.4 Defining Minimum and Maximum Density
A minimum density,
min , is determined by oven-drying and pulverizing the soil to
a single-grain structure, then slowly pouring it through a funnel into a container
of known volume. The soil must be dry to prevent bulking.
Figure 13.9
Vibrating table for
obtaining a
standardized
maximum density
of granular soils.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.