Page 23 - Geothermal Energy Renewable Energy and The Environment
P. 23
Introduction 5
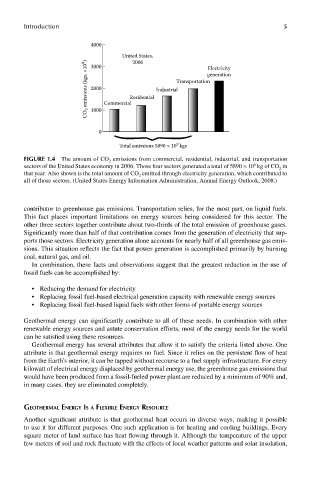
4000
United States, Electricity
2006
CO 2 emissions (kgs, ×10 9 ) 2000 Commercial Residential Industrial Transportation generation
3000
1000
0
9
Total emissions 5890 × 10 kgs
FIGUre 1.4 The amount of CO 2 emissions from commercial, residential, industrial, and transportation
sectors of the United States economy in 2006. Those four sectors generated a total of 5890 × 10 kg of CO 2 in
9
that year. Also shown is the total amount of CO 2 emitted through electricity generation, which contributed to
all of those sectors. (United States Energy Information Administration, Annual Energy Outlook, 2008.)
contributor to greenhouse gas emissions. Transportation relies, for the most part, on liquid fuels.
This fact places important limitations on energy sources being considered for this sector. The
other three sectors together contribute about two-thirds of the total emission of greenhouse gases.
Significantly more than half of that contribution comes from the generation of electricity that sup-
ports those sectors. Electricity generation alone accounts for nearly half of all greenhouse gas emis-
sions. This situation reflects the fact that power generation is accomplished primarily by burning
coal, natural gas, and oil.
In combination, these facts and observations suggest that the greatest reduction in the use of
fossil fuels can be accomplished by:
• Reducing the demand for electricity
• Replacing fossil fuel-based electrical generation capacity with renewable energy sources
• Replacing fossil fuel-based liquid fuels with other forms of portable energy sources
Geothermal energy can significantly contribute to all of these needs. In combination with other
renewable energy sources and astute conservation efforts, most of the energy needs for the world
can be satisfied using these resources.
Geothermal energy has several attributes that allow it to satisfy the criteria listed above. One
attribute is that geothermal energy requires no fuel. Since it relies on the persistent flow of heat
from the Earth’s interior, it can be tapped without recourse to a fuel supply infrastructure. For every
kilowatt of electrical energy displaced by geothermal energy use, the greenhouse gas emissions that
would have been produced from a fossil-fueled power plant are reduced by a minimum of 90% and,
in many cases, they are eliminated completely.
GeoThermal enerGy is a flexible enerGy resource
Another significant attribute is that geothermal heat occurs in diverse ways, making it possible
to use it for different purposes. One such application is for heating and cooling buildings. Every
square meter of land surface has heat flowing through it. Although the temperature of the upper
few meters of soil and rock fluctuate with the effects of local weather patterns and solar insolation,