Page 23 - Global Tectonics
P. 23
10 CHAPTER 2
2.1 EARTHQUAKE on the Richter scale implies a 30-fold increase in energy
release (Stein & Wysession, 2003).
SEISMOLOGY
2.1.3 Seismic waves
2.1.1 Introduction
The strain energy released by an earthquake is transmit-
ted through the Earth by several types of seismic wave
Much of our knowledge of the internal constitution of
(Fig. 2.2), which propagate by elastic deformation of
the Earth has come from the study of the seismic
the rock through which they travel. Waves penetrating
waves generated by earthquakes. These waves follow
the interior of the Earth are known as body waves, and
various paths through the interior of the Earth, and by
consist of two types corresponding to the two possible
measuring their travel times to different locations
ways of deforming a solid medium. P waves, also known
around the globe it is possible to determine its large-
as longitudinal or compressional waves, correspond to
scale layering. It is also possible to make inferences
elastic deformation by compression/dilation. They
about the physical properties of these layers from a
consideration of the velocities with which they trans- cause the particles of the transmitting rock to oscillate
in the direction of travel of the wave so that the distur-
mit the seismic waves.
bance proceeds as a series of compressions and rarefac-
tions. The velocity of a P wave V p is given by:
2.1.2 Earthquake descriptors 4
k + μ
V p = 3
Earthquakes are normally assumed to originate from a ρ
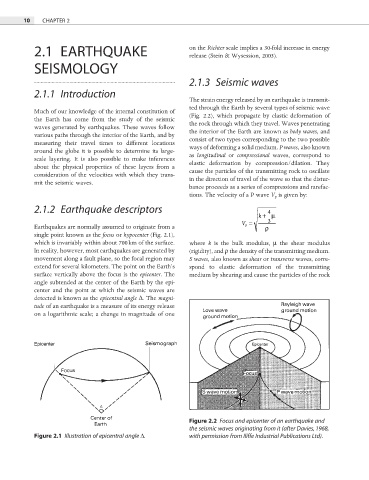
single point known as the focus or hypocenter (Fig. 2.1),
which is invariably within about 700 km of the surface. where k is the bulk modulus, μ the shear modulus
In reality, however, most earthquakes are generated by (rigidity), and ρ the density of the transmitting medium.
movement along a fault plane, so the focal region may S waves, also known as shear or transverse waves, corre-
extend for several kilometers. The point on the Earth’s spond to elastic deformation of the transmitting
surface vertically above the focus is the epicenter. The medium by shearing and cause the particles of the rock
angle subtended at the center of the Earth by the epi-
center and the point at which the seismic waves are
detected is known as the epicentral angle Δ. The magni-
tude of an earthquake is a measure of its energy release
on a logarithmic scale; a change in magnitude of one
Figure 2.2 Focus and epicenter of an earthquake and
the seismic waves originating from it (after Davies, 1968,
Figure 2.1 Illustration of epicentral angle Δ. with permission from Iliffe Industrial Publications Ltd).