Page 360 - Global Tectonics
P. 360
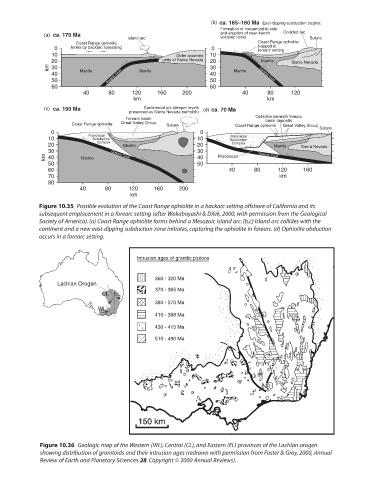
(b) ca. 165–160 Ma East-dipping subduction begins:
Formation of metamorphic sole
(a) ca. 170 Ma and eruption of near-trench Collided arc
Island arc volcanic rocks Suture
Coast Range ophiolite Coast Range ophiolite
0 forms by backarc spreading 0 trapped in
forearc setting
10 Older accreted 10
20 units of Sierra Nevada 20 Mantle Sierra Nevada
km 30 Mantle Mantle 30 Mantle
40 Oceanic Crust 40 Oceanic Crust
50 50
60 60
40 80 120 160 200 40 80 120
km km
(c) ca. 100 Ma Continental arc (deeper levels (d) ca. 70 Ma
preserved as Sierra Nevada batholith)
Forearc basin: Ophiolite beneath forearc
basin deposits
Coast Range ophiolite Great Valley Group Suture Coast Range ophiolite Great Valley Group
0 Franciscan 0 Suture
10 Subduction 10 Franciscan
Subduction
20 Complex Mantle 20 Complex Mantle Sierra Nevada
30 30
km 40 Mantle Oceanic Crust 40 Franciscan Oceanic Crust
50 50
60 40 80 120 160
70 km
80
40 80 120 160 200
km
Figure 10.35 Possible evolution of the Coast Range ophiolite in a backarc setting offshore of California and its
subsequent emplacement in a forearc setting (after Wakabayashi & Dilek, 2000, with permission from the Geological
Society of America). (a) Coast Range ophiolite forms behind a Mesozoic island arc. (b,c) Island arc collides with the
continent and a new east-dipping subduction zone initiates, capturing the ophiolite in forearc. (d) Ophiolite obduction
occurs in a forearc setting.
Intrusion ages of granitic plutons
360 - 320 Ma
Lachlan Orogen
370 - 365 Ma
CL EL
380 - 370 Ma
WL
410 - 398 Ma
430 - 415 Ma
510 - 490 Ma
Figure 10.36 Geologic map of the Western (WL), Central (CL), and Eastern (EL) provinces of the Lachlan orogen
showing distribution of granitoids and their intrusion ages (redrawn with permission from Foster & Gray, 2000, Annual
Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences 28. Copyright © 2000 Annual Reviews).