Page 395 - Global Tectonics
P. 395
PRECAMBRIAN TECTONICS AND THE SUPERCONTINENT CYCLE 377
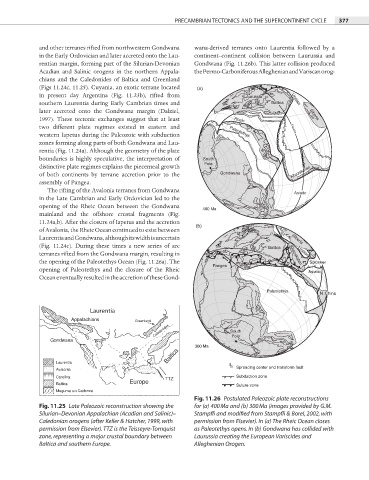
and other terranes rifted from northwestern Gondwana wana-derived terranes onto Laurentia followed by a
in the Early Ordovician and later accreted onto the Lau- continent–continent collision between Laurussia and
rentian margin, forming part of the Silurian-Devonian Gondwana (Fig. 11.26b). This latter collision produced
Acadian and Salinic orogens in the northern Appala- the Permo-Carboniferous Alleghenian and Variscan orog-
chians and the Caledonides of Baltica and Greenland
(Figs 11.24c, 11.25). Cuyania, an exotic terrane located (a)
in present day Argentina (Fig. 11.23b), rifted from Laurussia
southern Laurentia during Early Cambrian times and Baltica Uralian
later accreted onto the Gondwana margin (Dalziel, Siberia
1997). These tectonic exchanges suggest that at least Rheic
two different plate regimes existed in eastern and Equator
Equator
western Iapetus during the Paleozoic with subduction Paleotethys
zones forming along parts of both Gondwana and Lau-
rentia (Fig. 11.24a). Although the geometry of the plate
boundaries is highly speculative, the interpretation of South
Pole
distinctive plate regimes explains the piecemeal growth
of both continents by terrane accretion prior to the Gondwana Khazakstan
assembly of Pangea.
The rifting of the Avalonia terranes from Gondwana Asiatic
in the Late Cambrian and Early Ordovician led to the
opening of the Rheic Ocean between the Gondwana 400 Ma
mainland and the offshore crustal fragments (Fig.
11.24a,b). After the closure of Iapetus and the accretion
(b)
of Avalonia, the Rheic Ocean continued to exist between Anjui
Laurentia and Gondwana, although its width is uncertain Siberia
(Fig. 11.24c). During these times a new series of arc Baltica
terranes rifted from the Gondwana margin, resulting in Equator Khazakstan
Uralian
Equator
the opening of the Paleotethys Ocean (Fig. 11.26a). The Solonker
Pangea
opening of Paleotethys and the closure of the Rheic Asiatic
Ocean eventually resulted in the accretion of these Gond-
Paleotethys
N. China
Laurentia
Appalachians Greenland
Caledonides South
Pole
Gondwana
300 Ma
Baltica
Laurentia
Spreading center and transform fault
Avalonia
Carolina TTZ Subduction zone
Europe
Baltica Suture zone
Meguma and Cadomia
Fig. 11.26 Postulated Paleozoic plate reconstructions
Fig. 11.25 Late Paleozoic reconstruction showing the for (a) 400 Ma and (b) 300 Ma (images provided by G.M.
Silurian–Devonian Appalachian (Acadian and Salinic)– Stampfli and modified from Stampfli & Borel, 2002, with
Caledonian orogens (after Keller & Hatcher, 1999, with permission from Elsevier). In (a) The Rheic Ocean closes
permission from Elsevier). TTZ is the Teisseyre-Tornquist as Paleotethys opens. In (b) Gondwana has collided with
zone, representing a major crustal boundary between Laurussia creating the European Variscides and
Baltica and southern Europe. Alleghenian Orogen.