Page 145 - Glucose Monitoring Devices
P. 145
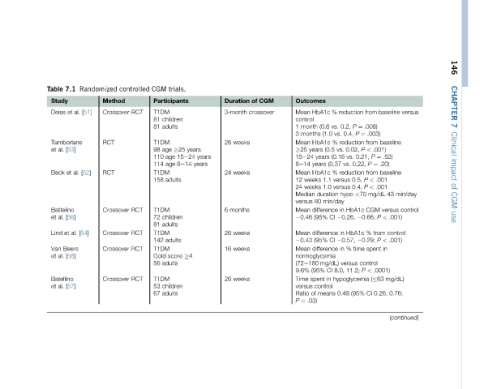
146 CHAPTER 7 Clinical impact of CGM use
versus min/day control (continued)
baseline baseline .52) .20) baseline .001 .001 43 versus .001) < control .001) < in .0001) mg/dL) 0.76; 0.26,
from .008) .003) ¼ from .001) < P ¼ P 0.21, ¼ P from < P < P mg/dL <70 CGM P 0.66; from % P 0.29; spent control < P ( 63 CI
reduction ¼ P 0.2, P 0.4, reduction 0.02, vs. 0.22, vs. reduction 0.5, 0.4, hypo HbA1c 0.26, HbA1c 0.57, time % versus 11.2; hypoglycemia (95% 0.49
% vs. (0.6 vs. (1.0 % vs. (0.5 (0.18 (0.37 % versus 1.1 versus 1.0 duration min/day in difference CI in difference CI in difference mg/dL) 8.0, CI in control means
Outcomes HbA1c Mean control month 1 months 3 HbA1c Mean years 25 years 15e24 years 8e14 HbA1c Mean weeks 12 weeks 24 Median 80 versus Mean (95% 0.46 Mean (95% 0.43 Mean normoglycemia (72e180 (95% 9.6% spent Time versus of Ratio .03) ¼ P
CGM crossover
of
Duration 3-month weeks 26 weeks 24 months 6 weeks 26 weeks 16 weeks 26
years years
years 15e24 4
trials. Participants children adults 25 age 8e14 age adults children adults adults score adults children adults
CGM T1DM 81 81 T1DM age 98 110 114 T1DM 158 T1DM 72 81 T1DM 142 T1DM Gold 56 T1DM 53 67
controlled RCT Crossover RCT Crossover RCT Crossover RCT Crossover RCT Crossover
Randomized Method [51] RCT RCT [52]
7.1 al. et Tamborlane [53] al. et Battelino [56] [54] al. et Beers [58] [57]
Table Study Deiss al. et Beck al. et Lind Van al. et Batellino al. et