Page 252 - Glucose Monitoring Devices
P. 252
Low glucose suspend system 259
Therefore, reducing hypoglycemia should be the first goal of the closed-loop system
and may be accomplished by suspending insulin delivery when a predetermined low
glucose level is reached [29].
The low glucose suspend (LGS, alternatively called threshold suspend (TS) in
the United States) feature suspends insulin delivery when the glucose sensor value
nears a programmed lower threshold (unless the patient overrides the alarm/alert)
with the aim of reducing the severity of hypoglycemic events. Pump suspension lasts
for 2 h in absence of user intervention, but the pump can be manually restarted at any
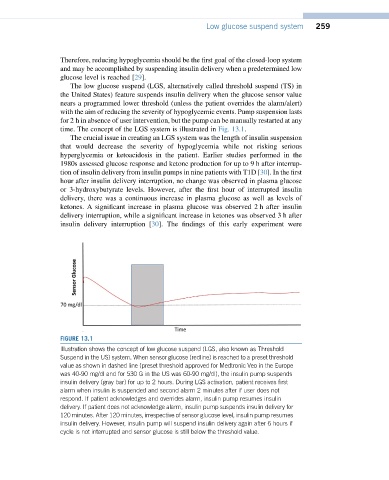
time. The concept of the LGS system is illustrated in Fig. 13.1.
The crucial issue in creating an LGS system was the length of insulin suspension
that would decrease the severity of hypoglycemia while not risking serious
hyperglycemia or ketoacidosis in the patient. Earlier studies performed in the
1980s assessed glucose response and ketone production for up to 9 h after interrup-
tion of insulin delivery from insulin pumps in nine patients with T1D [30]. In the first
hour after insulin delivery interruption, no change was observed in plasma glucose
or 3-hydroxybutyrate levels. However, after the first hour of interrupted insulin
delivery, there was a continuous increase in plasma glucose as well as levels of
ketones. A significant increase in plasma glucose was observed 2 h after insulin
delivery interruption, while a significant increase in ketones was observed 3 h after
insulin delivery interruption [30]. The findings of this early experiment were
FIGURE 13.1
Illustration shows the concept of low glucose suspend (LGS, also known as Threshold
Suspend in the US) system. When sensor glucose (redline) is reached to a preset threshold
value as shown in dashed line (preset threshold approved for Medtronic Veo in the Europe
was 40-90 mg/dl and for 530 G in the US was 60-90 mg/dl), the insulin pump suspends
insulin delivery (gray bar) for up to 2 hours. During LGS activation, patient receives first
alarm when insulin is suspended and second alarm 2 minutes after if user does not
respond. If patient acknowledges and overrides alarm, insulin pump resumes insulin
delivery. If patient does not acknowledge alarm, insulin pump suspends insulin delivery for
120 minutes. After 120 minutes, irrespective of sensor glucose level, insulin pump resumes
insulin delivery. However, insulin pump will suspend insulin delivery again after 6 hours if
cycle is not interrupted and sensor glucose is still below the threshold value.