Page 260 -
P. 260
D
C h a p t e r 1 1 : h a p t e r 1 1 :
C D a t a c e n t e r D e s i g n a n d R e d e s i g n a t a c e n t e r D e s i g n a n d R e d e s i g n 231 231
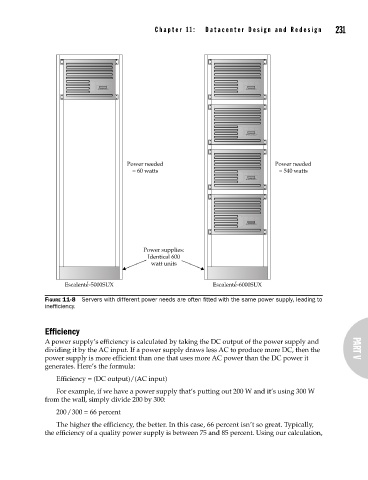
Power needed Power needed
= 60 watts = 540 watts
Power supplies:
Identical 600
watt units
Escalente ′ -5000SUX Escalente ′ -6000SUX
FIGURE 11-8 Servers with different power needs are often fitted with the same power supply, leading to
inefficiency.
Efficiency
A power supply’s efficiency is calculated by taking the DC output of the power supply and
dividing it by the AC input. If a power supply draws less AC to produce more DC, then the PART V
power supply is more efficient than one that uses more AC power than the DC power it
generates. Here’s the formula:
Efficiency = (DC output)/(AC input)
For example, if we have a power supply that’s putting out 200 W and it’s using 300 W
from the wall, simply divide 200 by 300:
200/300 = 66 percent
The higher the efficiency, the better. In this case, 66 percent isn’t so great. Typically,
the efficiency of a quality power supply is between 75 and 85 percent. Using our calculation,