Page 62 -
P. 62
C C h a p t e r 2 : h a p t e r 2 : C C u r r e n t I n i t i a t i v e s a n d S t a n d a r d s u r r e n t I n i t i a t i v e s a n d S t a n d a r d s 33 33
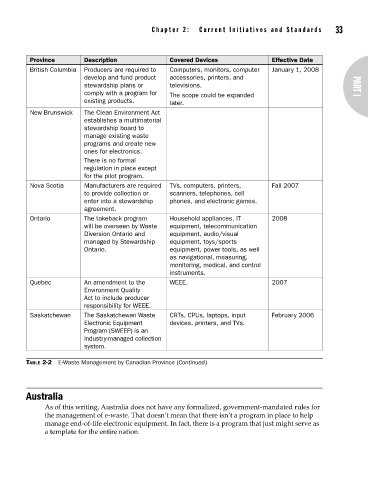
Province Description Covered Devices Effective Date
British Columbia Producers are required to Computers, monitors, computer January 1, 2008
develop and fund product accessories, printers, and
stewardship plans or televisions. PART I
comply with a program for The scope could be expanded
PART I
PART I
existing products. later.
New Brunswick The Clean Environment Act
establishes a multimaterial
stewardship board to
manage existing waste
programs and create new
ones for electronics.
There is no formal
regulation in place except
for the pilot program.
Nova Scotia Manufacturers are required TVs, computers, printers, Fall 2007
to provide collection or scanners, telephones, cell
enter into a stewardship phones, and electronic games.
agreement.
Ontario The takeback program Household appliances, IT 2008
will be overseen by Waste equipment, telecommunication
Diversion Ontario and equipment, audio/visual
managed by Stewardship equipment, toys/sports
Ontario. equipment, power tools, as well
as navigational, measuring,
monitoring, medical, and control
instruments.
Quebec An amendment to the WEEE. 2007
Environment Quality
Act to include producer
responsibility for WEEE.
Saskatchewan The Saskatchewan Waste CRTs, CPUs, laptops, input February 2006
Electronic Equipment devices, printers, and TVs.
Program (SWEEP) is an
industry-managed collection
system.
TABLE 2-2 E-Waste Management by Canadian Province (Continued)
Australia
As of this writing, Australia does not have any formalized, government-mandated rules for
the management of e-waste. That doesn’t mean that there isn’t a program in place to help
manage end-of-life electronic equipment. In fact, there is a program that just might serve as
a template for the entire nation.