Page 173 -
P. 173
The Beginning and the End? • 147
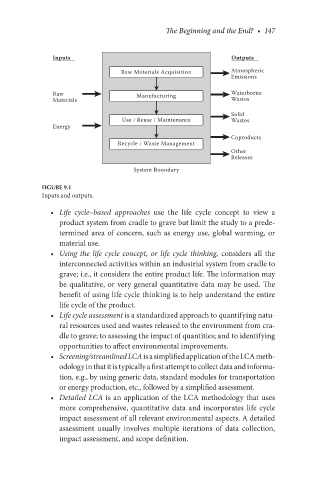
Inputs Outputs
Raw Materials Acquisition Atmospheric
Emissions
Raw Manufacturing Waterborne
Materials Wastes
Solid
Use / Reuse / Maintenance Wastes
Energy
Coproducts
Recycle / Waste Management
Other
Releases
System Boundary
Figure 9.1
Inputs and outputs.
• Life cycle–based approaches use the life cycle concept to view a
product system from cradle to grave but limit the study to a prede-
termined area of concern, such as energy use, global warming, or
material use.
• Using the life cycle concept, or life cycle thinking, considers all the
interconnected activities within an industrial system from cradle to
grave; i.e., it considers the entire product life. The information may
be qualitative, or very general quantitative data may be used. The
benefit of using life cycle thinking is to help understand the entire
life cycle of the product.
• Life cycle assessment is a standardized approach to quantifying natu-
ral resources used and wastes released to the environment from cra-
dle to grave; to assessing the impact of quantities; and to identifying
opportunities to affect environmental improvements.
• Screening/streamlined LCA is a simplified application of the LCA meth-
odology in that it is typically a first attempt to collect data and informa-
tion, e.g., by using generic data, standard modules for transportation
or energy production, etc., followed by a simplified assessment.
• Detailed LCA is an application of the LCA methodology that uses
more comprehensive, quantitative data and incorporates life cycle
impact assessment of all relevant environmental aspects. A detailed
assessment usually involves multiple iterations of data collection,
impact assessment, and scope definition.