Page 61 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 61
44 Chapter 2 - Introduction to Portland Cement Concrete
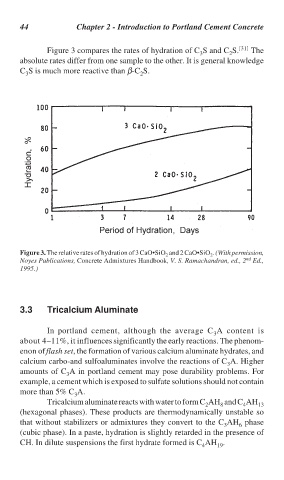
Figure 3 compares the rates of hydration of C S and C S. [31] The
2
3
absolute rates differ from one sample to the other. It is general knowledge
C S is much more reactive than β-C S.
2
3
Figure 3. The relative rates of hydration of 3 CaO•SiO and 2 CaO•SiO . (With permission,
2
2
nd
Noyes Publications, Concrete Admixtures Handbook, V. S. Ramachandran, ed., 2 Ed.,
1995.)
3.3 Tricalcium Aluminate
In portland cement, although the average C A content is
3
about 4–11%, it influences significantly the early reactions. The phenom-
enon of flash set, the formation of various calcium aluminate hydrates, and
calcium carbo-and sulfoaluminates involve the reactions of C A. Higher
3
amounts of C A in portland cement may pose durability problems. For
3
example, a cement which is exposed to sulfate solutions should not contain
more than 5% C A.
3
Tricalcium aluminate reacts with water to form C AH and C AH 13
4
8
2
(hexagonal phases). These products are thermodynamically unstable so
that without stabilizers or admixtures they convert to the C AH phase
6
3
(cubic phase). In a paste, hydration is slightly retarded in the presence of
CH. In dilute suspensions the first hydrate formed is C AH .
4
19