Page 172 - HVAC Pump Handbook
P. 172
Rishel_CH06.qxd 20/4/06 6:06 PM Page 169
HVAC Pump Performance
HVAC Pump Performance 169
6.7.2 Pump noise within the pump
Much of the objectionable noise coming from a pump installation orig-
inates within the pump itself. There are two basic causes for internal
pump noise, namely, improper selection or operation. Both of these
are caused by operating the pump far from the best efficiency curve
for a pump. The following description of noise sources will describe
how noise is generated within the pump.
Internal pump noise comes from: (1) mechanical losses; (2) hydraulic
loss caused by the water flowing through the impeller and casing, and
(3) circulation loss caused by water flowing past the tongue or cut
water of the pump. Figure 6.4 describes these losses. Obviously, noise
is a form of energy, so a noisy pump is usually an inefficient pump.
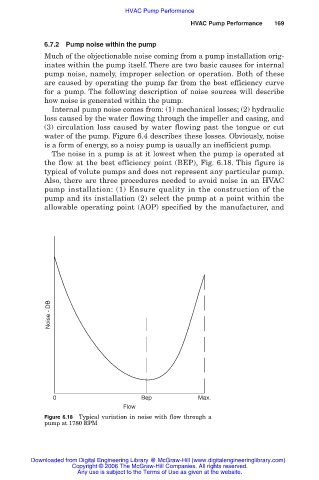
The noise in a pump is at it lowest when the pump is operated at
the flow at the best efficiency point (BEP), Fig. 6.18. This figure is
typical of volute pumps and does not represent any particular pump.
Also, there are three procedures needed to avoid noise in an HVAC
pump installation: (1) Ensure quality in the construction of the
pump and its installation (2) select the pump at a point within the
allowable operating point (AOP) specified by the manufacturer, and
Noise - DB
0 Bep Max.
Flow
Figure 6.18 Typical variation in noise with flow through a
pump at 1780 RPM
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2006 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.