Page 114 - Hacking Roomba
P. 114
Chapter 5 — Driving Roomba 95
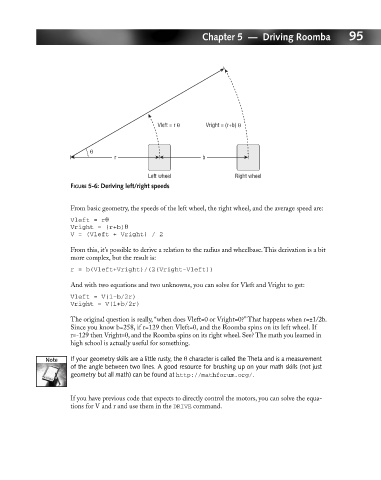
Vleft = r θ Vright = (r+b) θ
θ
r b
Left wheel Right wheel
FIGURE 5-6: Deriving left/right speeds
From basic geometry, the speeds of the left wheel, the right wheel, and the average speed are:
Vleft = rθ
Vright = (r+b)θ
V = (Vleft + Vright) / 2
From this, it’s possible to derive a relation to the radius and wheelbase. This derivation is a bit
more complex, but the result is:
r = b(Vleft+Vright)/(2(Vright-Vleft))
And with two equations and two unknowns, you can solve for Vleft and Vright to get:
Vleft = V(1-b/2r)
Vright = V(1+b/2r)
The original question is really, “when does Vleft=0 or Vright=0?” That happens when r=±1/2b.
Since you know b=258, if r=129 then Vleft=0, and the Roomba spins on its left wheel. If
r=-129 then Vright=0, and the Roomba spins on its right wheel. See? The math you learned in
high school is actually useful for something.
If your geometry skills are a little rusty, the θ character is called the Theta and is a measurement
of the angle between two lines. A good resource for brushing up on your math skills (not just
geometry but all math) can be found at http://mathforum.org/.
If you have previous code that expects to directly control the motors, you can solve the equa-
tions for V and r and use them in the DRIVE command.