Page 124 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 124
Section 6.0 - Hydration 107
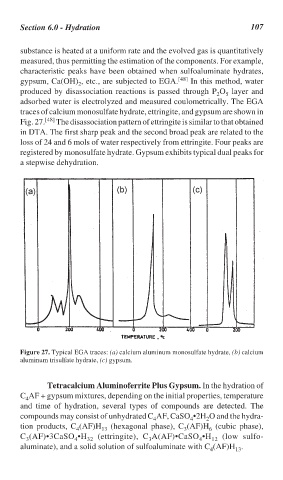
substance is heated at a uniform rate and the evolved gas is quantitatively
measured, thus permitting the estimation of the components. For example,
characteristic peaks have been obtained when sulfoaluminate hydrates,
gypsum, Ca(OH) , etc., are subjected to EGA. [48] In this method, water
2
produced by disassociation reactions is passed through P O layer and
2
5
adsorbed water is electrolyzed and measured coulometrically. The EGA
traces of calcium monosulfate hydrate, ettringite, and gypsum are shown in
Fig. 27. [48] The disassociation pattern of ettringite is similar to that obtained
in DTA. The first sharp peak and the second broad peak are related to the
loss of 24 and 6 mols of water respectively from ettringite. Four peaks are
registered by monosulfate hydrate. Gypsum exhibits typical dual peaks for
a stepwise dehydration.
Figure 27. Typical EGA traces: (a) calcium aluminum monosulfate hydrate, (b) calcium
aluminum trisulfate hydrate, (c) gypsum.
Tetracalcium Aluminoferrite Plus Gypsum. In the hydration of
C AF + gypsum mixtures, depending on the initial properties, temperature
4
and time of hydration, several types of compounds are detected. The
compounds may consist of unhydrated C AF, CaSO •2H O and the hydra-
4 4 2
tion products, C (AF)H (hexagonal phase), C (AF)H (cubic phase),
3
6
4
13
C (AF)•3CaSO •H (ettringite), C A(AF)•CaSO •H (low sulfo-
3 4 32 3 4 12
aluminate), and a solid solution of sulfoaluminate with C (AF)H .
13
4