Page 247 - Handbook of Thermal Analysis of Construction Materials
P. 247
228 Chapter 6 - Retarding and Water Reducing Admixtures
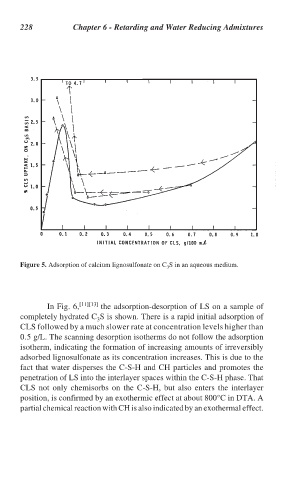
Figure 5. Adsorption of calcium lignosulfonate on C S in an aqueous medium.
3
In Fig. 6, [11][13] the adsorption-desorption of LS on a sample of
completely hydrated C S is shown. There is a rapid initial adsorption of
3
CLS followed by a much slower rate at concentration levels higher than
0.5 g/L. The scanning desorption isotherms do not follow the adsorption
isotherm, indicating the formation of increasing amounts of irreversibly
adsorbed lignosulfonate as its concentration increases. This is due to the
fact that water disperses the C-S-H and CH particles and promotes the
penetration of LS into the interlayer spaces within the C-S-H phase. That
CLS not only chemisorbs on the C-S-H, but also enters the interlayer
position, is confirmed by an exothermic effect at about 800°C in DTA. A
partial chemical reaction with CH is also indicated by an exothermal effect.