Page 69 - Handbook of Adhesion Promoters
P. 69
62 Substrates - Surface Condition and Treat-
faces, improve bonding and wettability,
polymerize layers or graft functional
groups on the surface of materials. The
examples below characterize some changes
in the properties of surfaces which were
achieved by controlled experiments
selected for this section.
Plasma treatments are effective ways
of increasing the usually poor surface prop-
2
erties of polymers. The surface modifica-
tion is done without changing the bulk in
2
environmentally friendly manner. Forma-
tion of hydroxyl groups is one of the typical
outcomes which induces hydrophilic prop-
erties to otherwise hydrophobic surface of
polymers and increases their wettability. 2
Functional groups which are also known to
increase adhesion include C=O, COOH,
2
and OOH. As a result of formation of these
groups, a short plasma treatment (less than
6 s) can have higher bond strength than that
2
achieved with primer deposition. A low or
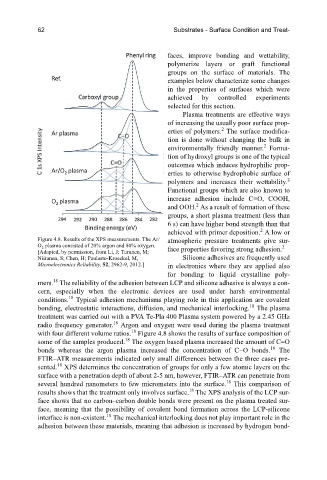
Figure 4.8. Results of the XPS measurements. The Ar/ atmospheric pressure treatments give sur-
O 2 plasma consisted of 20% argon and 80% oxygen. face properties favoring strong adhesion.
2
[Adapted, by permission, from Li, J; Turunen, M;
Niiranen, S; Chen, H; Paulasto-Kroeckel, M, Silicone adhesives are frequently used
Microelectronics Reliability, 52, 2962-9, 2012.] in electronics where they are applied also
for bonding to liquid crystalline poly-
18
mers. The reliability of the adhesion between LCP and silicone adhesive is always a con-
cern, especially when the electronic devices are used under harsh environmental
18
conditions. Typical adhesion mechanisms playing role in this application are covalent
18
bonding, electrostatic interactions, diffusion, and mechanical interlocking. The plasma
treatment was carried out with a PVA Te-Pla 400 Plasma system powered by a 2.45 GHz
18
radio frequency generator. Argon and oxygen were used during the plasma treatment
18
with four different volume ratios. Figure 4.8 shows the results of surface composition of
18
some of the samples produced. The oxygen based plasma increased the amount of C=O
18
bonds whereas the argon plasma increased the concentration of C−O bonds. The
FTIR–ATR measurements indicated only small differences between the three cases pre-
18
sented. XPS determines the concentration of groups for only a few atomic layers on the
surface with a penetration depth of about 2-5 nm, however, FTIR–ATR can penetrate from
18
several hundred nanometers to few micrometers into the surface. This comparison of
18
results shows that the treatment only involves surface. The XPS analysis of the LCP sur-
face shows that no carbon–carbon double bonds were present on the plasma treated sur-
face, meaning that the possibility of covalent bond formation across the LCP-silicone
18
interface is non-existent. The mechanical interlocking does not play important role in the
adhesion between these materials, meaning that adhesion is increased by hydrogen bond-