Page 198 - Handbook of Adhesives and Sealants
P. 198
168 Chapter Four
of conditions. Good recovery is characteristic of high performance ad-
hesives.
Compression set characteristics are determined by first placing a
test specimen under load for a period of time at temperature and then
subjecting the specimen to cyclic testing. Such a test method has been
adopted in ASTM C 719 and specification C 920. With certain sealants,
e.g., polysulfides, it has been determined that compression set often
leads to failure in tension. 21,22
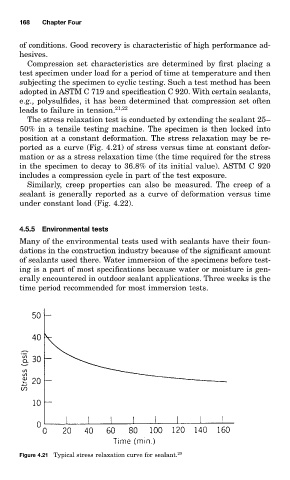
The stress relaxation test is conducted by extending the sealant 25–
50% in a tensile testing machine. The specimen is then locked into
position at a constant deformation. The stress relaxation may be re-
ported as a curve (Fig. 4.21) of stress versus time at constant defor-
mation or as a stress relaxation time (the time required for the stress
in the specimen to decay to 36.8% of its initial value). ASTM C 920
includes a compression cycle in part of the test exposure.
Similarly, creep properties can also be measured. The creep of a
sealant is generally reported as a curve of deformation versus time
under constant load (Fig. 4.22).
4.5.5 Environmental tests
Many of the environmental tests used with sealants have their foun-
dations in the construction industry because of the significant amount
of sealants used there. Water immersion of the specimens before test-
ing is a part of most specifications because water or moisture is gen-
erally encountered in outdoor sealant applications. Three weeks is the
time period recommended for most immersion tests.
Figure 4.21 Typical stress relaxation curve for sealant. 20