Page 258 - Handbook of Adhesives and Sealants
P. 258
Surfaces and Surface Preparation 227
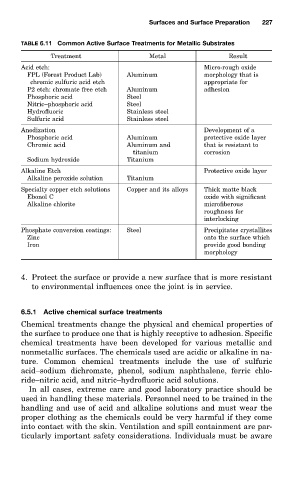
TABLE 6.11 Common Active Surface Treatments for Metallic Substrates
Treatment Metal Result
Acid etch: Micro-rough oxide
FPL (Forest Product Lab) Aluminum morphology that is
chromic sulfuric acid etch appropriate for
P2 etch: chromate free etch Aluminum adhesion
Phosphoric acid Steel
Nitric–phosphoric acid Steel
Hydrofluoric Stainless steel
Sulfuric acid Stainless steel
Anodization Development of a
Phosphoric acid Aluminum protective oxide layer
Chromic acid Aluminum and that is resistant to
titanium corrosion
Sodium hydroxide Titanium
Alkaline Etch Protective oxide layer
Alkaline peroxide solution Titanium
Specialty copper etch solutions Copper and its alloys Thick matte black
Ebonol C oxide with significant
Alkaline chlorite microfiberous
roughness for
interlocking
Phosphate conversion coatings: Steel Precipitates crystallites
Zinc onto the surface which
Iron provide good bonding
morphology
4. Protect the surface or provide a new surface that is more resistant
to environmental influences once the joint is in service.
6.5.1 Active chemical surface treatments
Chemical treatments change the physical and chemical properties of
the surface to produce one that is highly receptive to adhesion. Specific
chemical treatments have been developed for various metallic and
nonmetallic surfaces. The chemicals used are acidic or alkaline in na-
ture. Common chemical treatments include the use of sulfuric
acid–sodium dichromate, phenol, sodium naphthalene, ferric chlo-
ride–nitric acid, and nitric–hydrofluoric acid solutions.
In all cases, extreme care and good laboratory practice should be
used in handling these materials. Personnel need to be trained in the
handling and use of acid and alkaline solutions and must wear the
proper clothing as the chemicals could be very harmful if they come
into contact with the skin. Ventilation and spill containment are par-
ticularly important safety considerations. Individuals must be aware