Page 326 - Handbook of Adhesives and Sealants
P. 326
Adhesive Classifications 287
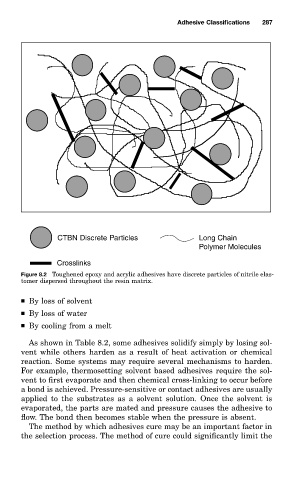
CTBN Discrete Particles Long Chain
Polymer Molecules
Crosslinks
Figure 8.2 Toughened epoxy and acrylic adhesives have discrete particles of nitrile elas-
tomer dispersed throughout the resin matrix.
By loss of solvent
By loss of water
By cooling from a melt
As shown in Table 8.2, some adhesives solidify simply by losing sol-
vent while others harden as a result of heat activation or chemical
reaction. Some systems may require several mechanisms to harden.
For example, thermosetting solvent based adhesives require the sol-
vent to first evaporate and then chemical cross-linking to occur before
a bond is achieved. Pressure-sensitive or contact adhesives are usually
applied to the substrates as a solvent solution. Once the solvent is
evaporated, the parts are mated and pressure causes the adhesive to
flow. The bond then becomes stable when the pressure is absent.
The method by which adhesives cure may be an important factor in
the selection process. The method of cure could significantly limit the