Page 366 - Handbook of Adhesives and Sealants
P. 366
322 Chapter Nine
An ingredient added to an adhesive to reduce the concentration of
base resin or binder is called a diluent. Diluents are principally used
to lower the viscosity and modify the processing conditions of some
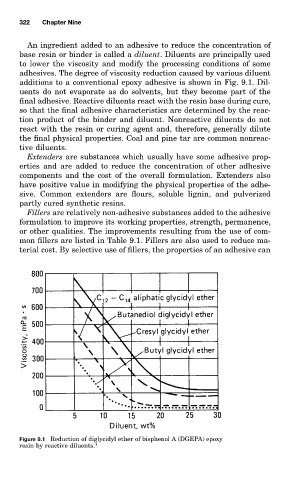
adhesives. The degree of viscosity reduction caused by various diluent
additions to a conventional epoxy adhesive is shown in Fig. 9.1. Dil-
uents do not evaporate as do solvents, but they become part of the
final adhesive. Reactive diluents react with the resin base during cure,
so that the final adhesive characteristics are determined by the reac-
tion product of the binder and diluent. Nonreactive diluents do not
react with the resin or curing agent and, therefore, generally dilute
the final physical properties. Coal and pine tar are common nonreac-
tive diluents.
Extenders are substances which usually have some adhesive prop-
erties and are added to reduce the concentration of other adhesive
components and the cost of the overall formulation. Extenders also
have positive value in modifying the physical properties of the adhe-
sive. Common extenders are flours, soluble lignin, and pulverized
partly cured synthetic resins.
Fillers are relatively non-adhesive substances added to the adhesive
formulation to improve its working properties, strength, permanence,
or other qualities. The improvements resulting from the use of com-
mon fillers are listed in Table 9.1. Fillers are also used to reduce ma-
terial cost. By selective use of fillers, the properties of an adhesive can
Figure 9.1 Reduction of diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A (DGEPA) epoxy
resin by reactive diluents. 1