Page 132 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 132
100 3 Structural Chemistry of Manganese Dioxide and Related Compounds
x in γ -MnO 2 ·nH 2 O ranges between 1.7 and 1.98; the ideal value of x = 2 cannot
be reached. Many methods are known for the preparation of γ -MnO 2 samples.
In general, most syntheses can be modified by the way in which γ -MnO 2 is
obtained. Samples of a good quality can be synthesized by oxidation of Mn (II)
salts with peroxodisulfates, permanganates, halogens, chlorates, bromates, and hy-
pohalogenates. Another preparation method is the reaction of permanganates with
organic or inorganic reducing agents (for a good collection of further references, see
Ref. [46]). More than 100 years of research on MnO 2 led to a huge variety of reaction
types, suitable for the production of manganese dioxide samples of widely differing
properties. Some CMD materials can be used as active battery components for
Le-clanch´ e cells or as catalysts; other samples may have ideal properties for organic
synthesis. However, the γ -modification of MnO 2 , regardless of the preparation
method (EMD or CMD), is one of most important basic, inorganic chemicals.
3.2.4
α-MnO 2
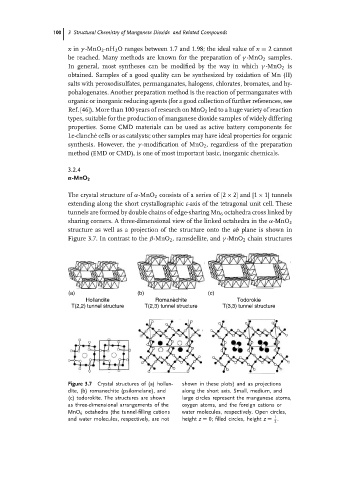
The crystal structure of α-MnO 2 consists of a series of [2 × 2] and [1 × 1] tunnels
extending along the short crystallographic c-axis of the tetragonal unit cell. These
tunnels are formed by double chains of edge-sharing Mn 6 octahedra cross linked by
sharing corners. A three-dimensional view of the linked octahedra in the α-MnO 2
structure as well as a projection of the structure onto the ab plane is shown in
Figure 3.7. In contrast to the β-MnO 2 , ramsdellite, and γ -MnO 2 chain structures
(a) (b) (c)
Hollandite Romanèchite Todorokie
T(2,2) tunnel structure T(2,3) tunnel structure T(3,3) tunnel structure
Figure 3.7 Crystal structures of (a) hollan- shown in these plots) and as projections
dite, (b) romanechite (psilomelane), and along the short axis. Small, medium, and
(c) todorokite. The structures are shown large circles represent the manganese atoms,
as three-dimensional arrangements of the oxygen atoms, and the foreign cations or
MnO 6 octahedra (the tunnel-filling cations water molecules, respectively. Open circles,
1
and water molecules, respectively, are not height z = 0; filled circles, height z = .
2