Page 365 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 365
11.3 Separators for Alkaline Storage Batteries 335
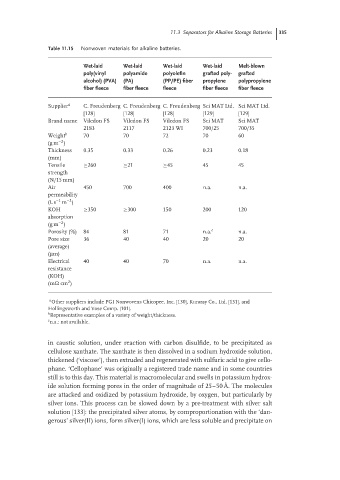
Table 11.15 Nonwoven materials for alkaline batteries.
Wet-laid Wet-laid Wet-laid Wet-laid Melt-blown
poly(vinyl polyamide polyolefin grafted poly- grafted
alcohol) (PVA) (PA) (PP/PE) fiber propylene polypropylene
fiber fleece fiber fleece fleece fiber fleece fiber fleece
Supplier a C. Freudenberg C. Freudenberg C. Freudenberg Sci MAT Ltd. Sci MAT Ltd.
[128] [128] [128] [129] [129]
Brand name Viledon FS Viledon FS Viledon FS Sci MAT Sci MAT
2183 2117 2123 WI 700/25 700/35
Weight b 70 70 72 70 60
–2
(g m )
Thickness 0.35 0.33 0.26 0.23 0.18
(mm)
Tensile ≥260 ≥21 ≥45 45 45
strength
(N/15 mm)
Air 450 700 400 n.a. n.a.
permeability
–2
(L s –1 m )
KOH ≥350 ≥300 150 200 120
absorption
–2
(g m )
Porosity (%) 84 81 71 n.a. c n.a.
Pore size 36 40 40 20 20
(average)
(µm)
Electrical 40 40 70 n.a. n.a.
resistance
(KOH)
2
(m cm )
a Other suppliers include PGI Nonwovens Chicopee, Inc. [130], Kuraray Co., Ltd. [131], and
Hollingsworth and Vose Comp. [101].
b Representative examples of a variety of weight/thickness.
c
n.a.: not available.
in caustic solution, under reaction with carbon disulfide, to be precipitated as
cellulose xanthate. The xanthate is then dissolved in a sodium hydroxide solution,
thickened (‘viscose’), then extruded and regenerated with sulfuric acid to give cello-
phane. ‘Cellophane’ was originally a registered trade name and in some countries
still is to this day. This material is macromolecular and swells in potassium hydrox-
ide solution forming pores in the order of magnitude of 25–50 ˚ A. The molecules
are attacked and oxidized by potassium hydroxide, by oxygen, but particularly by
silver ions. This process can be slowed down by a pre-treatment with silver salt
solution [133]: the precipitated silver atoms, by comproportionation with the ‘dan-
gerous’ silver(II) ions, form silver(I) ions, which are less soluble and precipitate on