Page 438 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 438
410 14 Lithium Alloy Anodes
Thus the variations of the electrode potential during discharge and charge, as
well as the phases present and the charge capacity of the electrode, directly reflect
the thermodynamics of the alloy system.
A series of experiments have been undertaken to evaluate the relevant thermo-
dynamic properties of a number of binary lithium alloy systems. The early work
◦
was directed toward determination of their behavior at about 400 C because of
interest in their potential use as components in molten salt batteries operating in
that general temperature range. Data for a number of binary lithium alloy systems
at about 400 C are presented in Table 14.1. These were mostly obtained by the use
◦
of an experimental arrangement employing the LiCl–KCl eutectic molten salt as a
lithium-conducting electrolyte.
It was shown some time ago that one can also use a similar thermodynamic
approach to explain and/or predict the composition dependence of the potential of
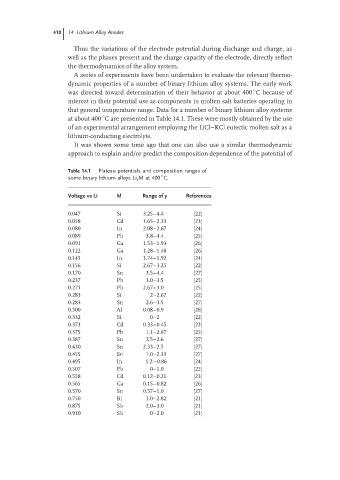
Table 14.1 Plateau potentials and composition ranges of
◦
some binary lithium alloys Li y M at 400 C.
Voltage vs Li M Range of y References
0.047 Si 3.25–4.4 [22]
0.058 Cd 1.65–2.33 [23]
0.080 In 2.08–2.67 [24]
0.089 Pb 3.8–4.4 [25]
0.091 Ga 1.53–1.93 [26]
0.122 Ga 1.28–1.48 [26]
0.145 In 1.74–1.92 [24]
0.156 Si 2.67–3.25 [22]
0.170 Sn 3.5–4.4 [27]
0.237 Pb 3.0–3.5 [25]
0.271 Pb 2.67–3.0 [25]
0.283 Si 2–2.67 [22]
0.283 Sn 2.6–3.5 [27]
0.300 Al 0.08–0.9 [28]
0.332 Si 0–2 [22]
0.373 Cd 0.33–0.45 [23]
0.375 Pb 1.1–2.67 [25]
0.387 Sn 2.5–2.6 [27]
0.430 Sn 2.33–2.5 [27]
0.455 Sn 1.0–2.33 [27]
0.495 In 1.2−0.86 [24]
0.507 Pb 0–1.0 [25]
0.558 Cd 0.12–0.21 [23]
0.565 Ga 0.15–0.82 [26]
0.570 Sn 0.57–1.0 [27]
0.750 Bi 1.0–2.82 [21]
0.875 Sb 2.0–3.0 [21]
0.910 Sb 0–2.0 [21]