Page 625 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 625
17.4 Bulk Properties 599
5
4
κ / (mS/cm) 3
2
1
0 5 10 15 20 25
trial number
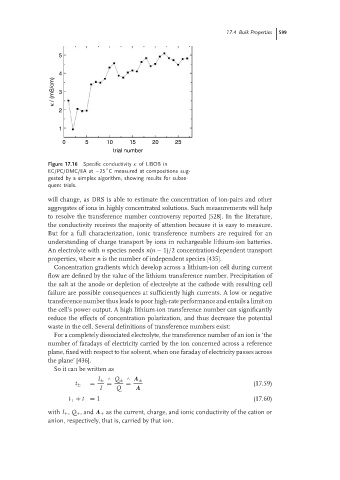
Figure 17.16 Specific conductivity κ of LiBOB in
◦
EC/PC/DMC/EA at −25 C measured at compositions sug-
gested by a simplex algorithm, showing results for subse-
quent trials.
will change, as DRS is able to estimate the concentration of ion-pairs and other
aggregates of ions in highly concentrated solutions. Such measurements will help
to resolve the transference number controversy reported [528]. In the literature,
the conductivity receives the majority of attention because it is easy to measure.
But for a full characterization, ionic transference numbers are required for an
understanding of charge transport by ions in rechargeable lithium-ion batteries.
An electrolyte with n species needs n(n − 1)/2 concentration-dependent transport
properties, where n is the number of independent species [435].
Concentration gradients which develop across a lithium-ion cell during current
flow are defined by the value of the lithium transference number. Precipitation of
the salt at the anode or depletion of electrolyte at the cathode with resulting cell
failure are possible consequences at sufficiently high currents. A low or negative
transference number thus leads to poor high-rate performance and entails a limit on
the cell’s power output. A high lithium-ion transference number can significantly
reduce the effects of concentration polarization, and thus decrease the potential
waste in the cell. Several definitions of transference numbers exist:
For a completely dissociated electrolyte, the transference number of an ion is ‘the
number of faradays of electricity carried by the ion concerned across a reference
plane, fixed with respect to the solvent, when one faraday of electricity passes across
the plane’ [436].
So it can be written as
I ± ∧ Q ± ∧ Λ ±
= = = (17.59)
t ±
I Q Λ
t + + t − = 1 (17.60)
with I ± , Q ± , and Λ ± as the current, charge, and ionic conductivity of the cation or
anion, respectively, that is, carried by that ion.