Page 659 - Handbook of Battery Materials
P. 659
18.2 Solvent-Free Polymer Electrolytes 633
64 32 16 10 6 3 2 1 EO/Li
250
200
3 2
PEO-LiN(SO 2 CF )
150
100
T (°C)
50
0
−50
Tg
100
0.0 0.2 3.4 0.6 0.8 1
W salt (weight fraction)
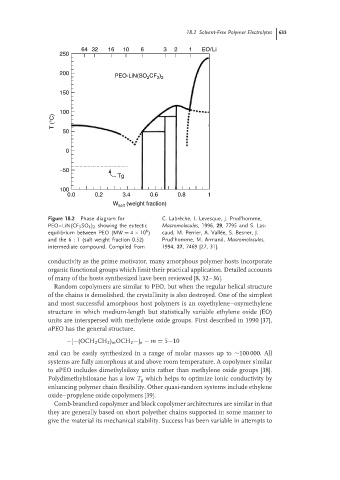
Figure 18.2 Phase diagram for C. Labr` eche, I. Levesque, J. Prud’homme,
PEO–LiN(CF 3 SO 3 ) 2 showing the eutectic Macromolecules, 1996, 29, 7795 and S. Las-
6
equilibrium between PEO (MW = 4 × 10 ) caud, M. Perrier, A. Vall´ ee, S. Besner, J.
and the 6 : 1 (salt weight fraction 0.52) Prud’homme, M. Armand, Macromolecules,
intermediate compound. Compiled from 1994, 27, 7469 [27, 31].
conductivity as the prime motivator, many amorphous polymer hosts incorporate
organic functional groups which limit their practical application. Detailed accounts
of many of the hosts synthesized have been reviewed [8, 32–36].
Random copolymers are similar to PEO, but when the regular helical structure
of the chains is demolished, the crystallinity is also destroyed. One of the simplest
and most successful amorphous host polymers is an oxyethylene–oxymethylene
structure in which medium-length but statistically variable ethylene oxide (EO)
units are interspersed with methylene oxide groups. First described in 1990 [37],
aPEO has the general structure.
−[−(OCH 2 CH 2 ) m OCH 2 −] n − m = 5−10
and can be easily synthesized in a range of molar masses up to ∼100 000. All
systems are fully amorphous at and above room temperature. A copolymer similar
to aPEO includes dimethylsiloxy units rather than methylene oxide groups [38].
Polydimethylsiloxane has a low T g which helps to optimize ionic conductivity by
enhancing polymer chain flexibility. Other quasi-random systems include ethylene
oxide–propylene oxide copolymers [39].
Comb-branched copolymer and block copolymer architectures are similar in that
they are generally based on short polyether chains supported in some manner to
give the material its mechanical stability. Success has been variable in attempts to