Page 120 - Handbook of Deep Learning in Biomedical Engineering Techniques and Applications
P. 120
108 Chapter 4 A critical review on using blockchain technology in education domain
• Broad gateway protocol (BGP) hijacks: As networks are
based on IP addresses, BGP hijacking is possible when
the hacker takes control of BGP router. Hacker falsely an-
nounces control of a group of IP addresses and reroutes
traffic to a new chain. This attack was launched against
MyEtherWallet.com
(g) Quantum attacks: BC uses public key digital signature algo-
rithms that are susceptible to attack by quantum algorithm
due to Shor’s algorithm. Hashing and secret key algorithms
also require larger key sizes to overcome attack by quantum
computing. To overcome this, postquantum cryptography
approaches such as lattice and code-based approaches can
be used.
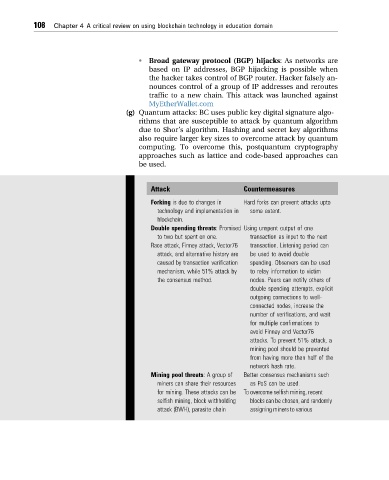
Attack Countermeasures
Forking is due to changes in Hard forks can prevent attacks upto
technology and implementation in some extent.
blockchain.
Double spending threats: Promised Using unspent output of one
to two but spent on one. transaction as input to the next
Race attack, Finney attack, Vector76 transaction. Listening period can
attack, and alternative history are be used to avoid double
caused by transaction verification spending. Observers can be used
mechanism, while 51% attack by to relay information to victim
the consensus method. nodes. Peers can notify others of
double spending attempts, explicit
outgoing connections to well-
connected nodes, increase the
number of verifications, and wait
for multiple confirmations to
avoid Finney and Vector76
attacks. To prevent 51% attack, a
mining pool should be prevented
from having more than half of the
network hash rate.
Mining pool threats: A group of Better consensus mechanisms such
miners can share their resources as PoS can be used.
for mining. These attacks can be To overcome selfish mining, recent
selfish mining, block withholding blocks can be chosen, and randomly
attack (BWH), parasite chain assigning miners to various