Page 149 - Handbook of Deep Learning in Biomedical Engineering Techniques and Applications
P. 149
138 Chapter 5 Depression discovery in cancer communities using deep learning
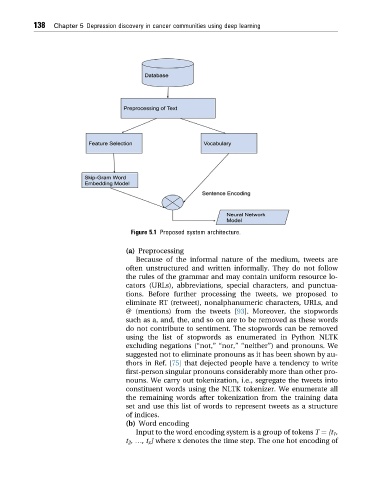
Figure 5.1 Proposed system architecture.
(a) Preprocessing
Because of the informal nature of the medium, tweets are
often unstructured and written informally. They do not follow
the rules of the grammar and may contain uniform resource lo-
cators (URLs), abbreviations, special characters, and punctua-
tions. Before further processing the tweets, we proposed to
eliminate RT (retweet), nonalphanumeric characters, URLs, and
@ (mentions) from the tweets [93]. Moreover, the stopwords
such as a, and, the, and so on are to be removed as these words
do not contribute to sentiment. The stopwords can be removed
using the list of stopwords as enumerated in Python NLTK
excluding negations (“not,”“nor,”“neither”) and pronouns. We
suggested not to eliminate pronouns as it has been shown by au-
thors in Ref. [75] that dejected people have a tendency to write
first-person singular pronouns considerably more than other pro-
nouns. We carry out tokenization, i.e., segregate the tweets into
constituent words using the NLTK tokenizer. We enumerate all
the remaining words after tokenization from the training data
set and use this list of words to represent tweets as a structure
of indices.
(b) Word encoding
Input to the word encoding system is a group of tokens T ¼ [t 1 ,
t 2 , .,t x ] where x denotes the time step. The one hot encoding of