Page 151 - Handbook of Deep Learning in Biomedical Engineering Techniques and Applications
P. 151
140 Chapter 5 Depression discovery in cancer communities using deep learning
t 0
W
W 0 0
t W
1 Generate W 1 So max O t
Context 1
Words Embedding Layer Averaging the Input
t W 2
2
W
W n-1
n-1
t
n-1
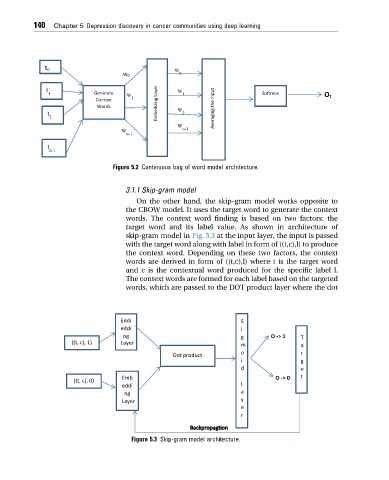
Figure 5.2 Continuous bag of word model architecture.
3.1.1 Skip-gram model
On the other hand, the skip-gram model works opposite to
the CBOW model. It uses the target word to generate the context
words. The context word finding is based on two factors: the
target word and its label value. As shown in architecture of
skip-gram model in Fig. 5.3 at the input layer, the input is passed
with the target word along with label in form of ((t,c),l) to produce
the context word. Depending on these two factors, the context
words are derived in form of ((t,c),l) where t is the target word
and c is the contextual word produced for the specific label l.
The context words are formed for each label based on the targeted
words, which are passed to the DOT product layer where the dot
Emb S
eddi i
ng g O -> 1 T
((t, c), 1) Layer m a
o r
Dot product
i g
d e
Emb O -> 0 t
((t, c), 0)
eddi L
ng a
Layer y
e
r
Figure 5.3 Skip-gram model architecture.