Page 315 - Handbook of Electronic Assistive Technology
P. 315
304 HANDBOOK OF ELECTRONIC ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY
Table 10-2 Advantages and Disadvantages of the Primary/Secondary Pass-Through
Model
Benefits Disadvantages
Minimises additional hardware. May be complex to set up.
Simpler maintenance requirement. Need for the user to understand a ‘long’ or other mode
press if using mode, and for the output control to be
compatible with this (i.e., does not require long switch
presses).
Potentially more seamless user experience as switch Need for user to understand signal ‘timeout’ if using this
input is ‘passed’ between devices. mode, and for the output control to be compatible with
this.
Can be complex to understand as user has to translate
input method to output method (e.g., switch scanning to
mouse movement).
User required to use primary device at all times.
Potential for output to become ‘stuck’ in secondary
device – i.e., if there is no built-in fail-safe mechanism.
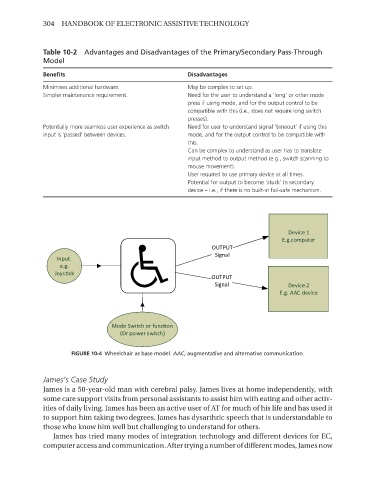
Device 1
E.g.computer
OUTPUT
Signal
Input.
e.g.
Joys ck
OUTPUT
Signal Device 2
E.g. AAC device
Mode Switch or func on
(Or power switch)
FIGURE 10-4 Wheelchair as base model� AAC, augmentative and alternative communication�
James’s Case Study
James is a 50-year-old man with cerebral palsy. James lives at home independently, with
some care support visits from personal assistants to assist him with eating and other activ-
ities of daily living. James has been an active user of AT for much of his life and has used it
to support him taking two degrees. James has dysarthric speech that is understandable to
those who know him well but challenging to understand for others.
James has tried many modes of integration technology and different devices for EC,
computer access and communication. After trying a number of different modes, James now