Page 319 - Handbook of Electronic Assistive Technology
P. 319
308 HANDBOOK OF ELECTRONIC ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY
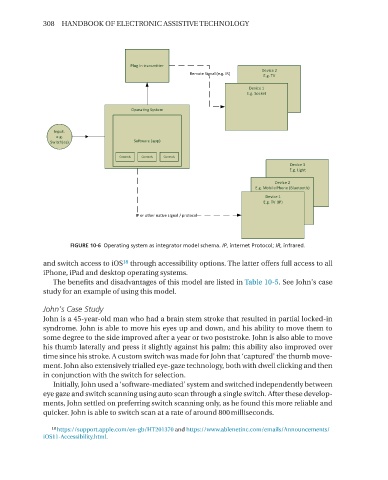
Plug In transmi er
Device 2
Remote Signal (e.g. IR) E.g. TV
Device 1
E.g. Socket
Opera ng System
Input.
e.g.
Switch(es) So ware (app)
Controls Controls Controls
Device 3
E.g. Light
Device 2
E.g. Mobile Phone (Bluetooth)
Device 1
E.g. TV (IP)
IP or other na ve signal / protocol
FIGURE 10-6 Operating system as integrator model schema� IP, internet Protocol; IR, infrared�
18
and switch access to iOS through accessibility options. The latter offers full access to all
iPhone, iPad and desktop operating systems.
The benefits and disadvantages of this model are listed in Table 10-5. See John’s case
study for an example of using this model.
John’s Case Study
John is a 45-year-old man who had a brain stem stroke that resulted in partial locked-in
syndrome. John is able to move his eyes up and down, and his ability to move them to
some degree to the side improved after a year or two poststroke. John is also able to move
his thumb laterally and press it slightly against his palm; this ability also improved over
time since his stroke. A custom switch was made for John that ‘captured’ the thumb move-
ment. John also extensively trialled eye-gaze technology, both with dwell clicking and then
in conjunction with the switch for selection.
Initially, John used a ‘software-mediated’ system and switched independently between
eye gaze and switch scanning using auto scan through a single switch. After these develop-
ments, John settled on preferring switch scanning only, as he found this more reliable and
quicker. John is able to switch scan at a rate of around 800 milliseconds.
18 https://support.apple.com/en-gb/HT201370 and https://www.ablenetinc.com/emails/Announcements/
iOS11-Accessibility.html.