Page 29 - Handbook of Energy Engineering Calculations
P. 29
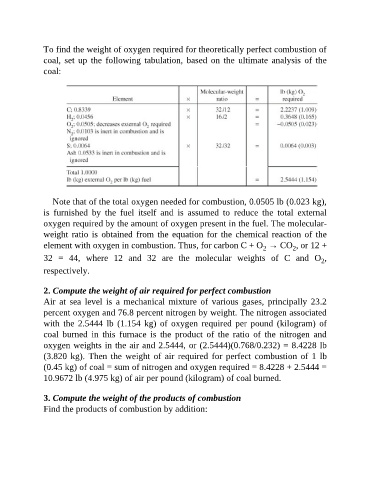
To find the weight of oxygen required for theoretically perfect combustion of
coal, set up the following tabulation, based on the ultimate analysis of the
coal:
Note that of the total oxygen needed for combustion, 0.0505 lb (0.023 kg),
is furnished by the fuel itself and is assumed to reduce the total external
oxygen required by the amount of oxygen present in the fuel. The molecular-
weight ratio is obtained from the equation for the chemical reaction of the
element with oxygen in combustion. Thus, for carbon C + O → CO , or 12 +
2
2
32 = 44, where 12 and 32 are the molecular weights of C and O ,
2
respectively.
2. Compute the weight of air required for perfect combustion
Air at sea level is a mechanical mixture of various gases, principally 23.2
percent oxygen and 76.8 percent nitrogen by weight. The nitrogen associated
with the 2.5444 lb (1.154 kg) of oxygen required per pound (kilogram) of
coal burned in this furnace is the product of the ratio of the nitrogen and
oxygen weights in the air and 2.5444, or (2.5444)(0.768/0.232) = 8.4228 lb
(3.820 kg). Then the weight of air required for perfect combustion of 1 lb
(0.45 kg) of coal = sum of nitrogen and oxygen required = 8.4228 + 2.5444 =
10.9672 lb (4.975 kg) of air per pound (kilogram) of coal burned.
3. Compute the weight of the products of combustion
Find the products of combustion by addition: