Page 30 - Handbook of Energy Engineering Calculations
P. 30
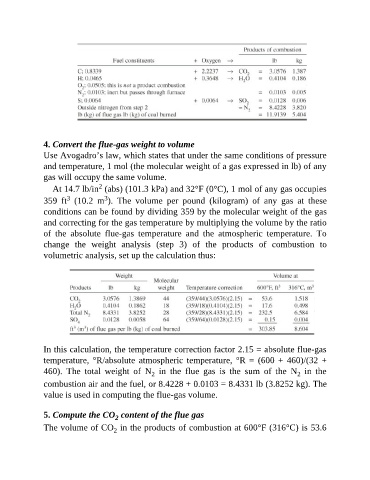
4. Convert the flue-gas weight to volume
Use Avogadro’s law, which states that under the same conditions of pressure
and temperature, 1 mol (the molecular weight of a gas expressed in lb) of any
gas will occupy the same volume.
2
At 14.7 lb/in (abs) (101.3 kPa) and 32°F (0°C), 1 mol of any gas occupies
3
3
359 ft (10.2 m ). The volume per pound (kilogram) of any gas at these
conditions can be found by dividing 359 by the molecular weight of the gas
and correcting for the gas temperature by multiplying the volume by the ratio
of the absolute flue-gas temperature and the atmospheric temperature. To
change the weight analysis (step 3) of the products of combustion to
volumetric analysis, set up the calculation thus:
In this calculation, the temperature correction factor 2.15 = absolute flue-gas
temperature, °R/absolute atmospheric temperature, °R = (600 + 460)/(32 +
460). The total weight of N in the flue gas is the sum of the N in the
2
2
combustion air and the fuel, or 8.4228 + 0.0103 = 8.4331 lb (3.8252 kg). The
value is used in computing the flue-gas volume.
5. Compute the CO content of the flue gas
2
The volume of CO in the products of combustion at 600°F (316°C) is 53.6
2