Page 321 - Handbook of Energy Engineering Calculations
P. 321
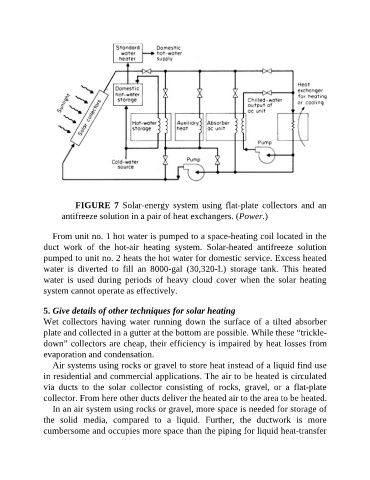
FIGURE 7 Solar-energy system using flat-plate collectors and an
antifreeze solution in a pair of heat exchangers. (Power.)
From unit no. 1 hot water is pumped to a space-heating coil located in the
duct work of the hot-air heating system. Solar-heated antifreeze solution
pumped to unit no. 2 heats the hot water for domestic service. Excess heated
water is diverted to fill an 8000-gal (30,320-L) storage tank. This heated
water is used during periods of heavy cloud cover when the solar heating
system cannot operate as effectively.
5. Give details of other techniques for solar heating
Wet collectors having water running down the surface of a tilted absorber
plate and collected in a gutter at the bottom are possible. While these “trickle-
down” collectors are cheap, their efficiency is impaired by heat losses from
evaporation and condensation.
Air systems using rocks or gravel to store heat instead of a liquid find use
in residential and commercial applications. The air to be heated is circulated
via ducts to the solar collector consisting of rocks, gravel, or a flat-plate
collector. From here other ducts deliver the heated air to the area to be heated.
In an air system using rocks or gravel, more space is needed for storage of
the solid media, compared to a liquid. Further, the ductwork is more
cumbersome and occupies more space than the piping for liquid heat-transfer