Page 193 - Handbook of Gold Exploration and Evaluation
P. 193
168 Handbook of gold exploration and evaluation
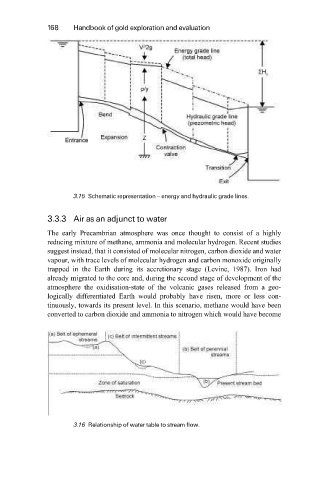
3.15 Schematic representation ± energy and hydraulic grade lines.
3.3.3 Air as an adjunct to water
The early Precambrian atmosphere was once thought to consist of a highly
reducing mixture of methane, ammonia and molecular hydrogen. Recent studies
suggest instead, that it consisted of molecular nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water
vapour, with trace levels of molecular hydrogen and carbon monoxide originally
trapped in the Earth during its accretionary stage (Levine, 1987). Iron had
already migrated to the core and, during the second stage of development of the
atmosphere the oxidisation-state of the volcanic gases released from a geo-
logically differentiated Earth would probably have risen, more or less con-
tinuously, towards its present level. In this scenario, methane would have been
converted to carbon dioxide and ammonia to nitrogen which would have become
3.16 Relationship of water table to stream flow.